316 Stainless Steel Elbow
Designed for durability and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for various industrial applications.
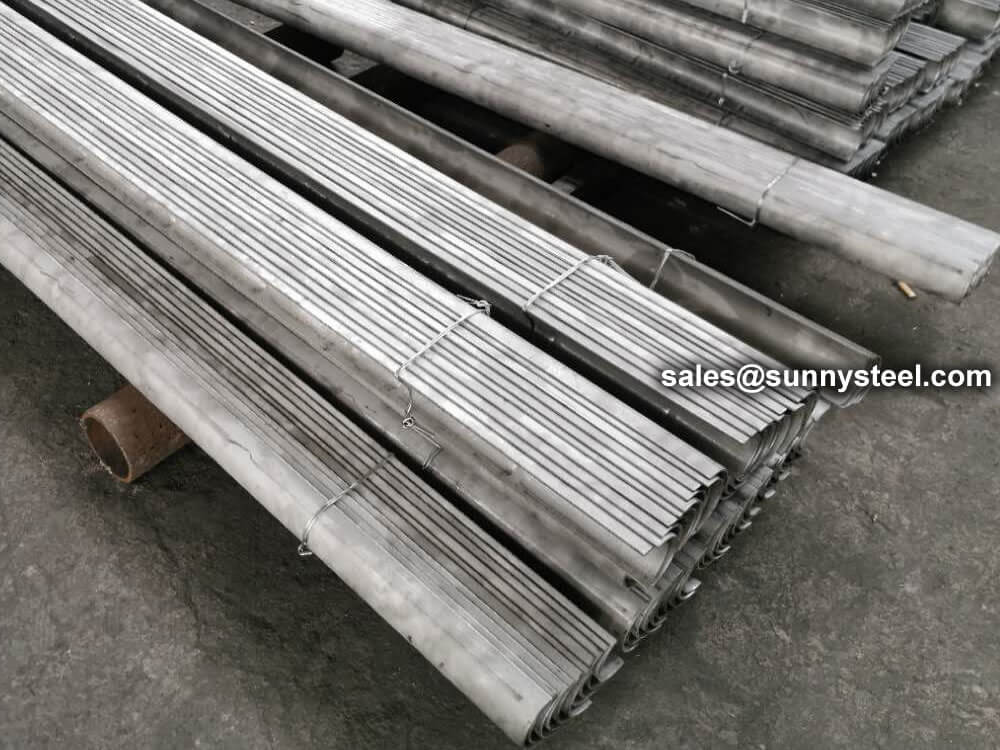

Stainless 316 Tube Shields are protective components designed to safeguard boiler tubes and high-temperature piping from erosion, corrosion, and wear, offering enhanced durability in severe industrial environments.
Download PDFStainless steel 316 (SS316) is an austenitic chromium-nickel stainless steel containing deliberate amount of molybdenum which increases general corrosion resistance and especially improves its pitting resistance to chloride ion solutions.
Grade 316 is the standard molybdenum-bearing grade, second in importance to 304 amongst the austenitic stainless steels. The molybdenum gives 316 better overall corrosion resistant properties than Grade 304, particularly higher resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion in chloride environments. 316L is best known among fabricators for being resistant to cracks after the weld process is completed. This makes 316L the preferred choice of fabricators who look to build metallic structures for industry applications.
Alloy 316/316L is an austenitic alloy and similar to 304/304L is used in a wide range of applications. It is an important alloy when it comes to chloride environments and many other chemical process industries. The addition of Molybdenum significantly increases general corrosion resistance as compared to 304/304L and more importantly, increases the chloride pitting resistance.
316/316L has excellent forming and welding characteristics. Due to its superior chloride pitting resistance, it is commonly used in applications involving chlorides or halides. That property is also useful in marine environments.
It also has an excellent resistance to intergranular corrosion in as-welded condition. Dual grade becomes important if heavy gauge welding is performed. This is where intergranular corrosion comes into picture and having a lower carbon version makes it difficult for Chromium Carbide to precipitate in the 797 to 1580 degF (425 to 860 degC) range when the welding is going on for a long time due to the heavy gauge.
It has excellent creep and rupture strength at higher temperatures compared to 304/304L. Finally, it has excellent strength and toughness at cryogenic temperatures.
In addition, it provides excellent elevated temperature tensile, creep and stress-rupture strengths.
| Grade | 316 | 316L |
|---|---|---|
| UNS Designation | S31600 | S31603 |
| Carbon (C) Max. | 0.08 | 0.030* |
| Manganese (Mn) Max. | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| Phosphorous (P) Max. | 0.045 | 0.045 |
| Sulphur (S) Max. | 0.030 | 0.030 |
| Silicon (Si) Max. | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Chromium (Cr) | 16.0 – 18.0 | 16.0 – 18.0 |
| Nickel (Ni) | 10.0 – 14.0 | 10.0 – 14.0 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 2.0 – 3.0 | 2.0 – 3.0 |
| Nitrogen (N) | — | — |
| Iron (Fe) | Bal. | Bal. |
| Other Elements | — | — |
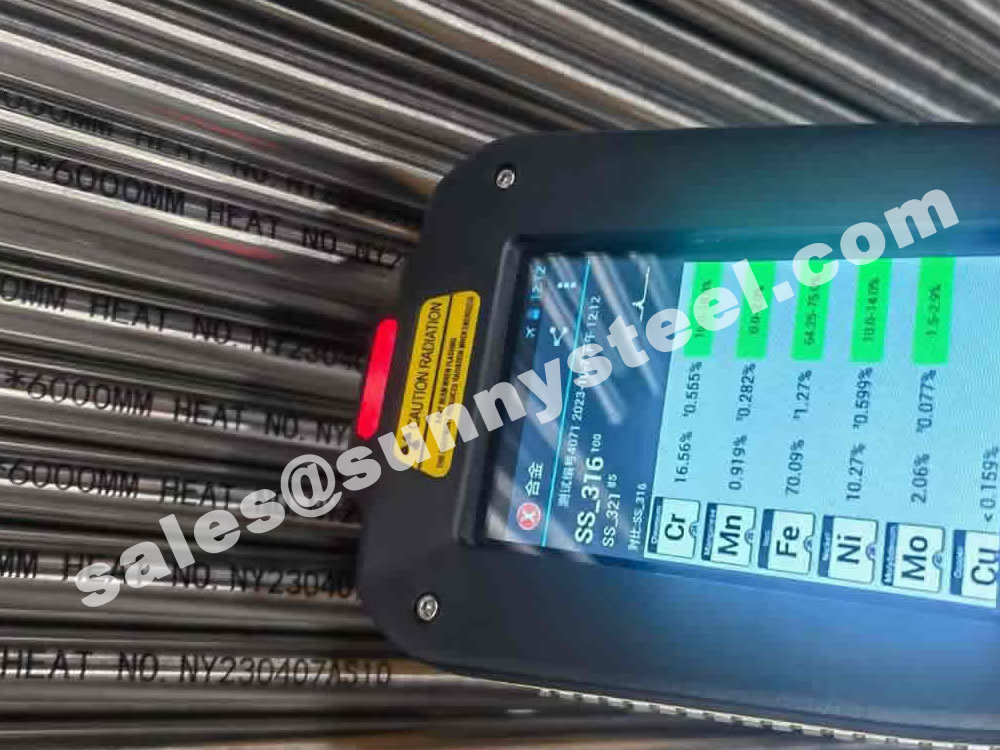
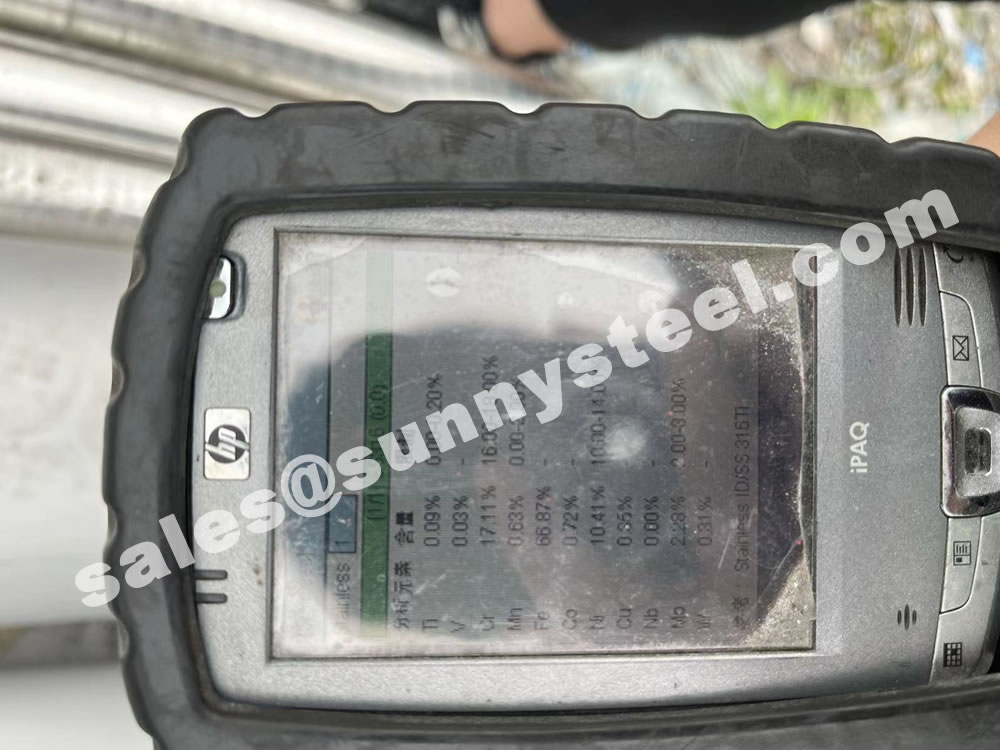

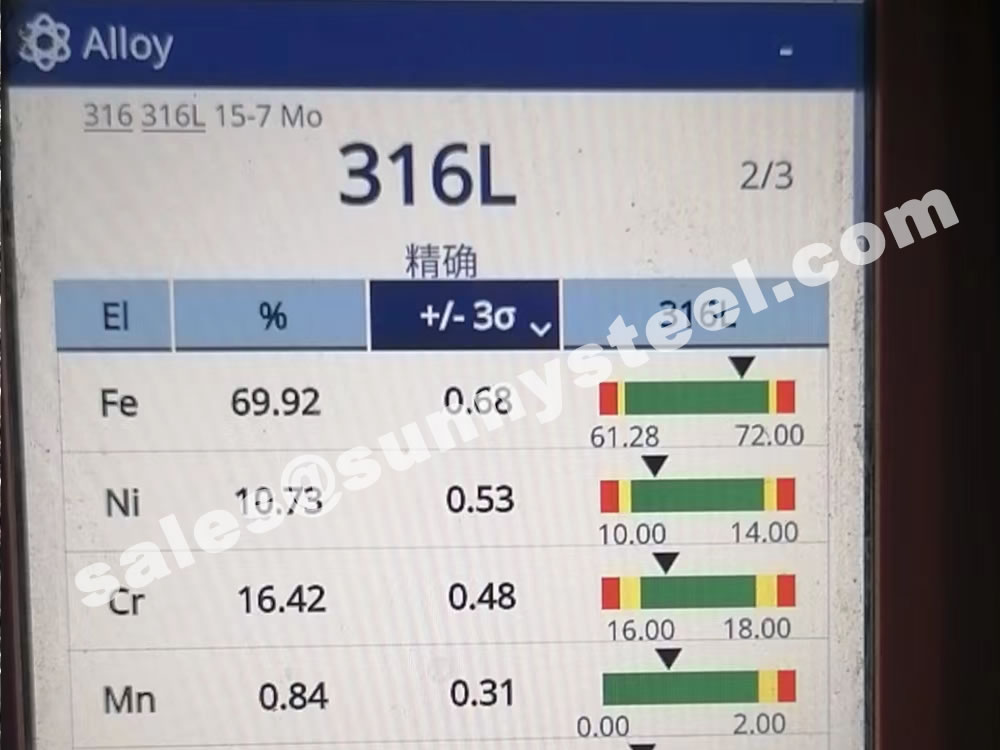

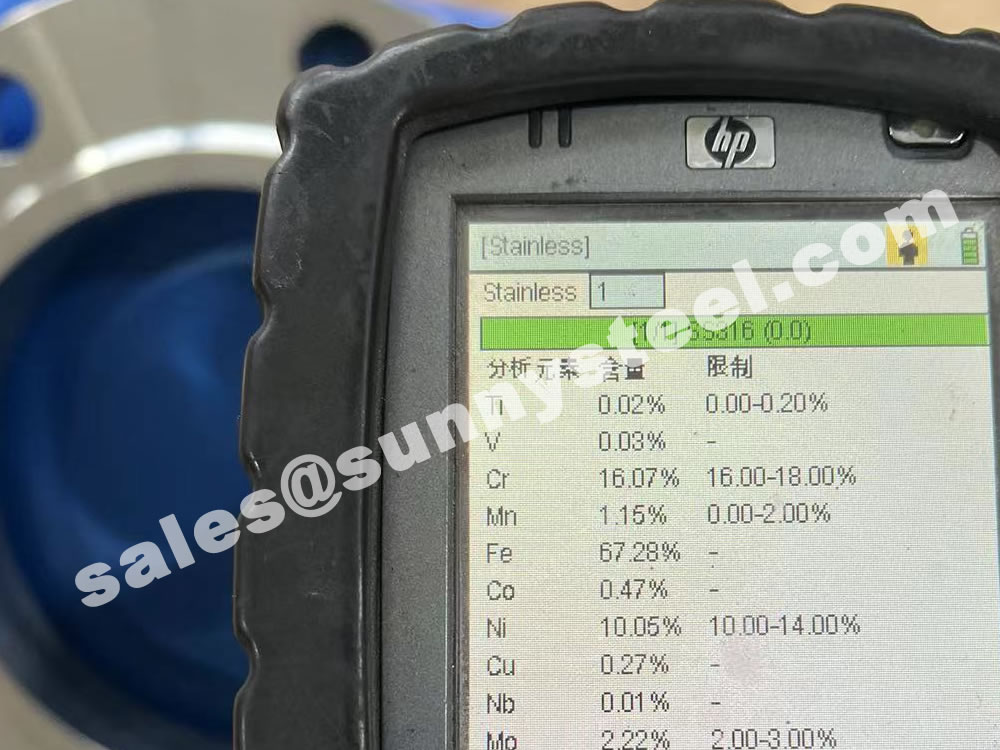

The main constituents of 316 stainless steel - other than iron - are Chromium and Nickel. However, it is the addition of 2% Molybdenum that provides the increased corrosion resistance.
316 contains 16 - 18% Chromium (Cr). Chromium is the essential chemical in all stainless steel and it is that which forms the thin passive layer that makes the metal "stainless"
316 also contains 10-14% Nickel (Ni). This is added to make the Austenitic structure more stable at normal temperatures.
The nickel also improves high-temperature oxidation resistance makes the steel resistant to stress corrosion cracking.
Where the steel is to be stretched formed a lower percentage (8%) of nickel should be selected. If the steel is to be deep drawn a higher percentage is better (9% or more).
In addition a number of other chemicals may be present but these are expressed as maximum permited levels with the exception of the increased quantity of carbon required in 316H - i.e. a minimum of .04% and a maximum of 0.10%
| Electrical Resistivity | Magnetic Permeability |
|---|---|
| 7.2e-005 ohm-cm | 1.008 |
| 7.2e-005 ohm-cm | 1.008 |
| at 20°C (68°F); 1.16E-04 at 650°C (1200°F) | at RT |
| Material | Form | Tensile Strength (ksi) |
Yield Strength (ksi) |
Elongation % |
Hardness HB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alloy 316L | 316L Sheet AMS 5507 | 100 max | - | 45 | - |
| Alloy 316 | 316 Sheet AMS 5524 | 75 min | 30 | 45 | 207 max |
316/316L/316H stainless steel in the Annealed Condition at -20°F to +100°F
| Alloy | UNS Designation | Spec. | Tensile Strength (psi) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Tensile Strength (ksi) | Yield Strength (psi) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Yield Strength (ksi) | Elongation in 2 inches (min.) % | Grain Size Req. | Max. Hardness | Modulus of Elasticity (x106 psi) | Mean Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (IN./IN./°F x 10-6) | Thermal Conductivity (BTU-in/ft2-h-°F) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 316 | S31600 | A249, A312 | 75,000 | 515 | 75 | 30,000 | 205 | 30 | 35 | — | 90 Rb | 28.0 | 9.2 | 116 |
| 316L | S31603 | A270, A312 | 70,000 | 485 | 70 | 25,000 | 170 | 25 | — | — | 90 Rb | 28.0 | 9.2 | 116 |
| 316H | S31609 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 7 or coarser | — | — | — | — |
| Alloy | UNS Designation | Werkstoff NR. | Specifications* |
|---|---|---|---|
| 316 | S31600 | 1.4401 | A269, A/SA249, A/SA312, A1016, A632, A/SA688 |
| 316L** | S31603 | 1.4404 | A269, A/SA249, A/SA312, A1016, A632, A/SA688 |
*Note: The specifications noted including ASTM, ASME, or other applicable authorities are correct at the time of publication. Other specifications may apply for use of these materials in different applications.
Type 316L is the low carbon version of 316 stainless. With the addition of molybdenum, the steel is popular for use in severe corrosion environments due to the materials immunity from boundary carbide precipitation (sensitisation).
The material is widely used in heavy gauge welded components and weld annealing is only required where the material is for use in high stress environments. 316L has an extensive variety of uses especially in marine applications due to the materials high corrosion resistance.
Type 316H is a higher carbon variant of 316 making the steel more suitable for use in applications where elevated temperatures are present.
Stabilised Grade 316Ti offers similar qualities.
The increased carbon content delivers a greater tensile and yield strength. The austenitic structure of the material also gives this grade excellent toughness, even down to cryogenic temperatures.
SS316 Stainless Steel Boiler Tube Shields are widely used in industrial boilers, power plants, and other high-temperature and high-pressure equipment.
Material: Stainless Steel 316 Size: Customized Surface Treatment: Polishing, Sandblasting, Electroplating, Powder Coating, Painting, etc.
The cross-sectional shape of boiler tubes shields is mostly semi-circular (180 degrees), and there are also 120-160 degrees.
It is mainly used on finned tubes (water-cooled walls); boiler tube erosion shields are divided into direct wear-resistant shields, in-curve, anti-wear shields, outer-curve, anti-wear shields, side-curve anti-wear shields, s-curve anti-wear shields, etc.
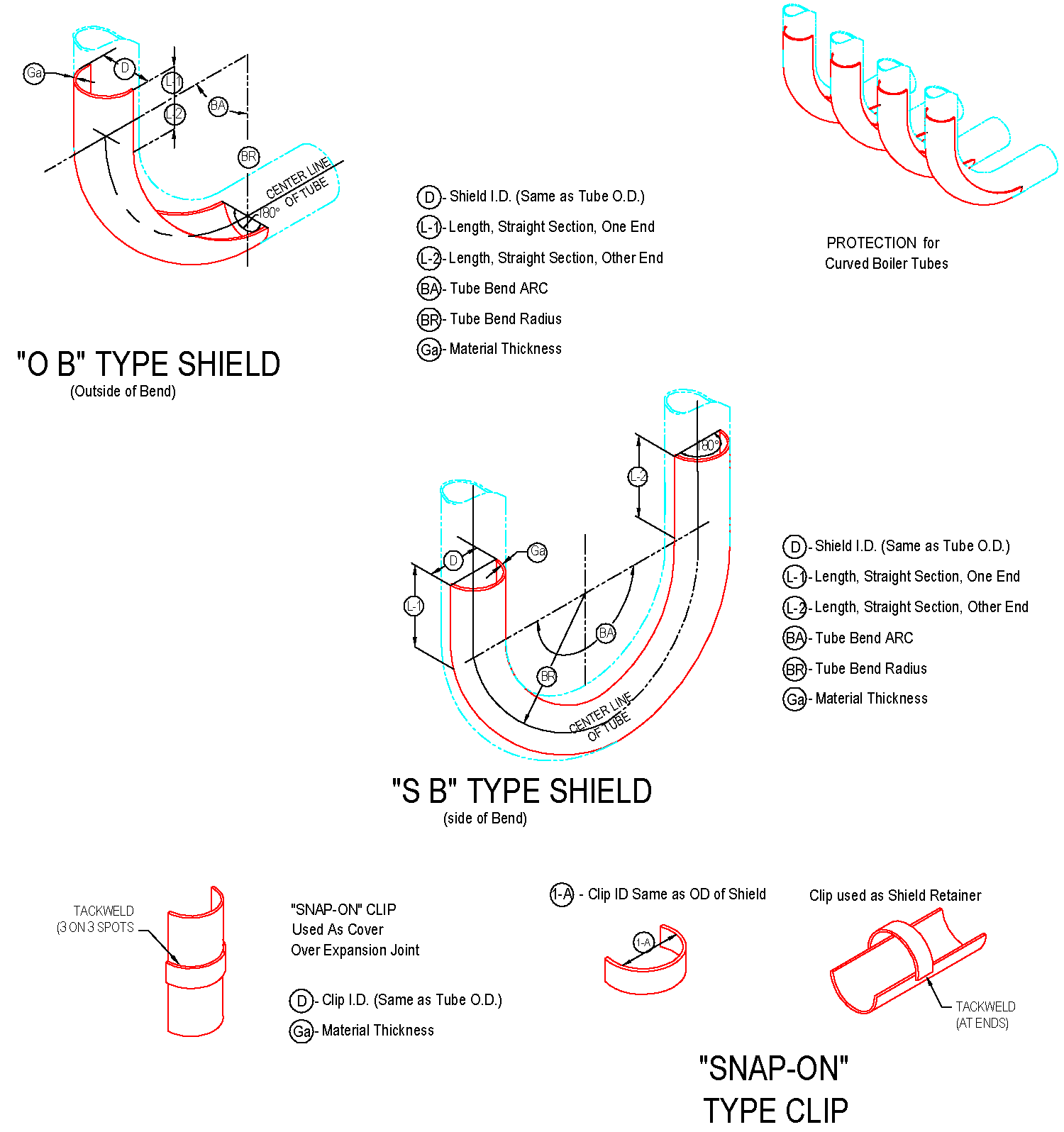
The length of the straight anti-wear shields ranges from 20mm to 3000mm, and the general length of 1000-2000mm is commonly used. The anti-wear shields with bends generally requires a processing drawing and the following parameters should be on the drawing: outer diameter of the pipe used, bending of the pipe Radius R (to the center of the pipe), the degree of bending angle, and the length of the straight sections on both sides of the arc segment of the wear-resistant shields.
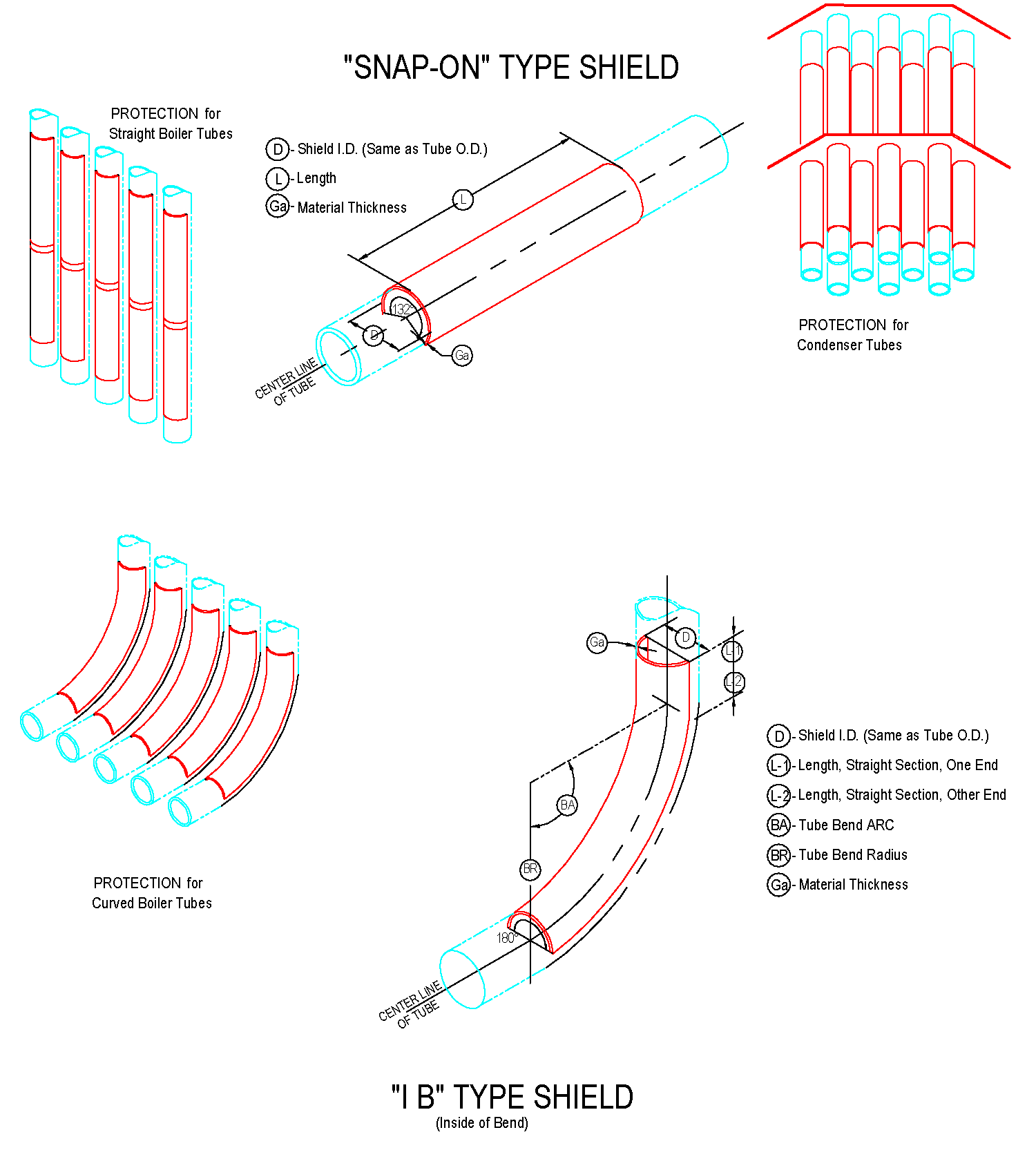
The most basic parameter of boiler tubes shields is the outer diameter of the tube used (that is, the inner diameter of boiler tubes erosion shields). The main specifications of the tube are: 32, 38, 42, 44.5, 48, 51, 57, 60, 63.5 , 76, 89mm, etc . the inner diameter of the boiler tubes erosion shields is usually 1-3mm larger than the outer diameter of the tube used, depending on the actual requirements.
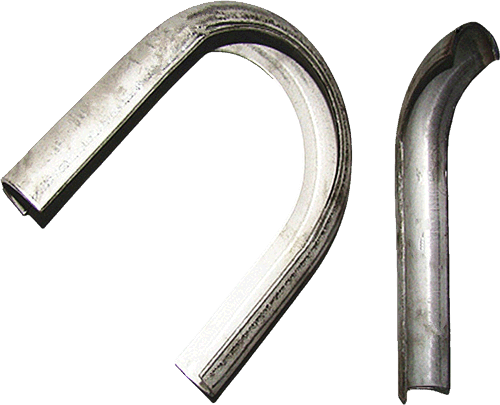
The current production process for tube shields is to use high-pressure presses and professional moulds for pressing.
Tube shields from us are manufactured to exacting standards. Advanced equipment and material handling capabilities permit us to offer the fastest turnaround times anywhere.
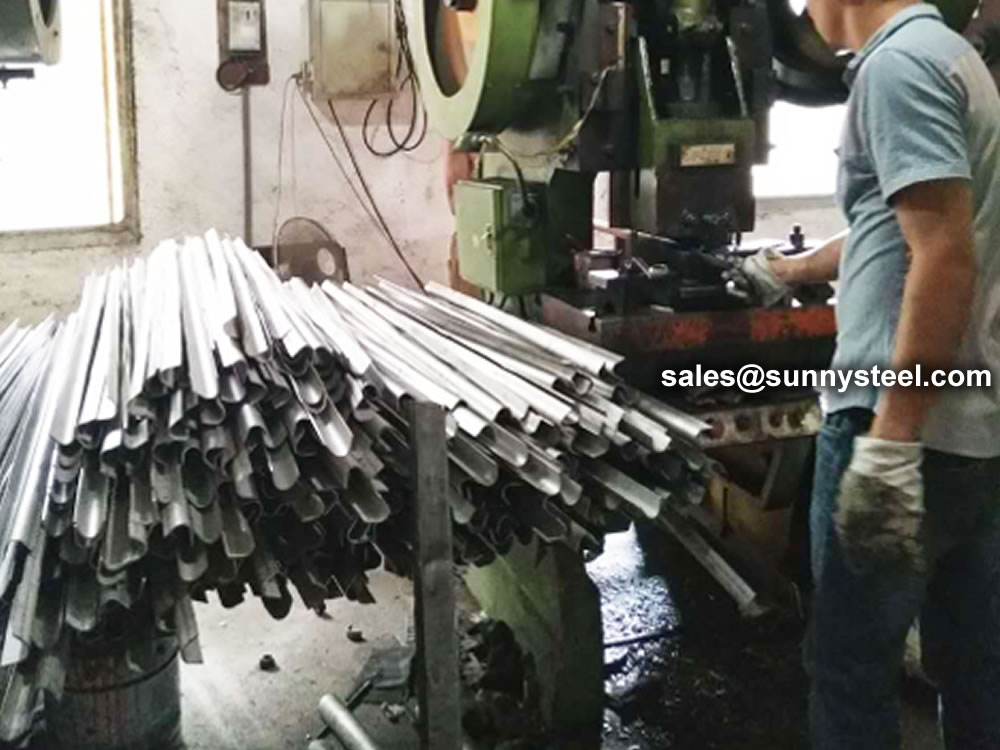

The current production process for tube shields is to use high-pressure presses and professional moulds for pressing.
The production time is short, the welding performance is good, the welding seam does not fall off, the surface is smooth and the appearance is beautiful. The arc-shaped wear-resistant tile is pressed on a press or bent on a pipe bender with a special mould.

To ensure the accuracy of the material. Positive Material Identification (PMI) of stainless steel sheets for tube shields is critical to verifying the grade and composition of stainless steel before it goes into production.
The raw materials for the production of tube shields are generally purchased directly from standard steel mills, and each batch has an MTC. Due to the sharpe limitations of raw materials, it is inevitable that excess materials will be produced. We can use the excess material to make a smaller size snap ring.
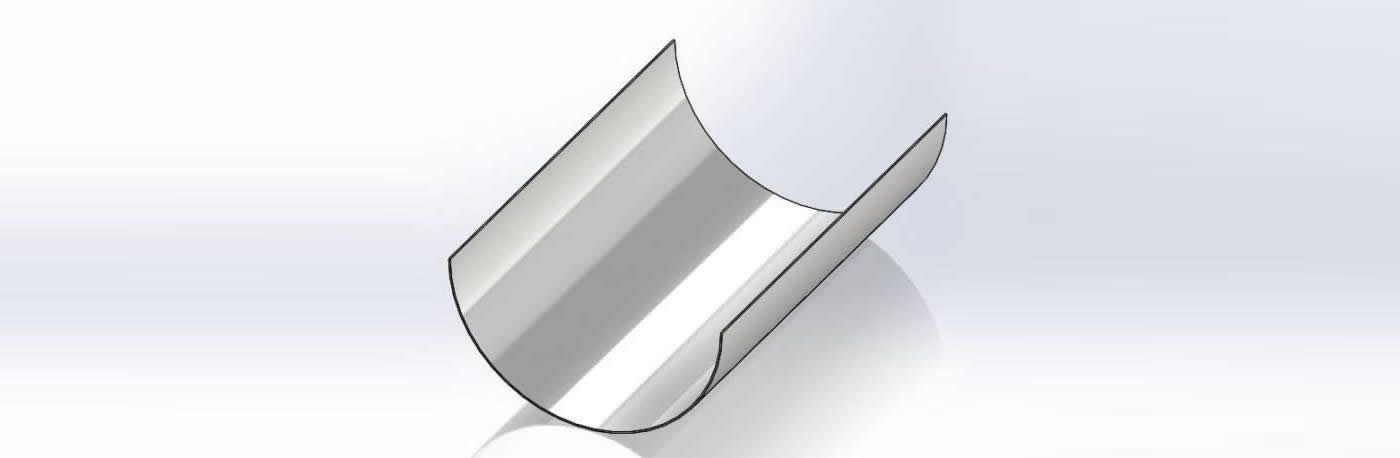
Different types of stainless steel are selected according to the specific conditions of different working conditions.
The boiler was originally designed to be accurate. Different materials have different temperature resistance and mechanical strength, generally has a temperature resistance of 600 ℃ or less.
We can also supply boiler tubes erosion shields of other materials.

Tube shields are custom made to fit perfectly to straight sections, curved sections and even finned and specialised tubing.
Boiler tube erosion shields, also known as anti-corrosion shields, anti-wear plate, anti-wear protection shields, anti-wear cover plate, anti-corrosion cover plate, boiler climbing pipe, anti-wear pressure plate, etc. , which are used in combination with snap rings.
Boiler tube erosion shields are produced using a high-pressure press and professional mould pressing. The production time is short, the welding performance is good, the welding should not fall off, the surface is smooth, and the appearance is beautiful. Boiler tube erosion shields with bends are formed by pressing on a press or bending with a special abrasive on a tube bender.
Boiler tube shields are designed to eliminate major maintenance and downtime costs from boiler and condenser tube failure.
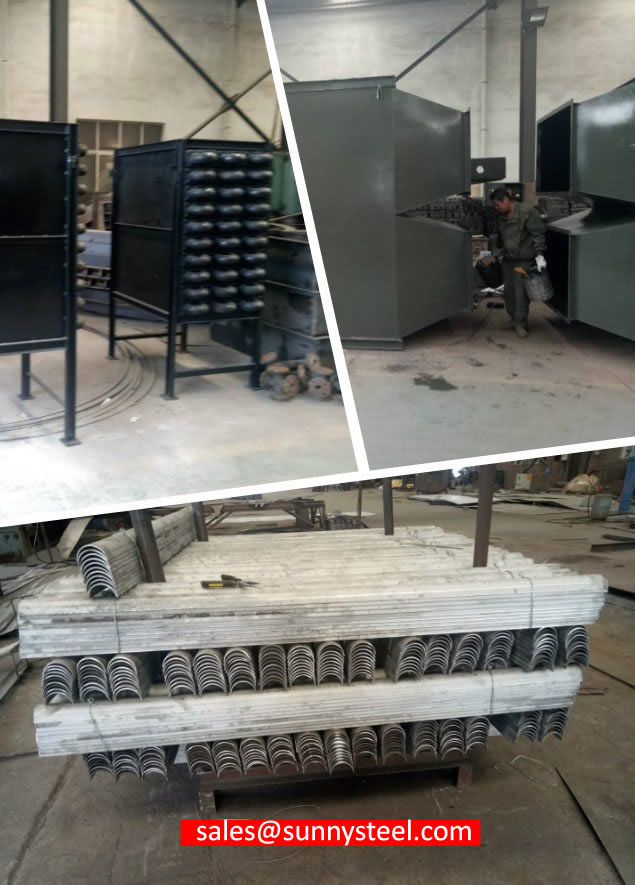

The service life of boiler tubes erosion shields is different in different types of boilers and different use parts.
The normal service life is a period of overhaul (3-5 years) for the boiler. Generally, some boilers will be replaced or retrofitted every time the boiler is overhauled. The main replacements are those of the Boiler Tubes Erosion Shields that are severely thinned and exceeded the standard; those that were not firmly detached during the boiler operation during the previous installation. According to the wear of the Boiler Tubes Erosion Shields during replacement, if the thickness is severely reduced, it needs to be replaced, the deformation is severe, and those that cannot protect the tube also need to be replaced. In addition, some boiler tubes are not equipped with Boiler Tubes Erosion Shields, but during the boiler inspection, it is found that the tubes have a tendency of wear and thinning. Generally, Boiler Tubes Erosion Shields are also installed to prevent further wear of the tubes and cause serious consequences such as boiler explosion.
On the heating surface of superheater and economizer tube bundle of the boiler, in order to prevent the pipe from being worn by high temperature flue gas washing, boiler tubes erosion shields are mostly arranged on the outer side of the pipe in the direction of flue gas flow. The elbow erosion shields solves the abrasion problems of water wall tubes, superheater tubes, economizer tubes and reheater tubes in the furnace, and provides guarantee for the long-term and reliable operation of CFB boiler. With the increase of CFB boiler products, the type and quantity of The elbow erosion shields will increase.
Our understanding of and commitment to the steam and power generation business enables us to solve your boiler tube erosion or corrosion problems efficiently. Our technical staff can quickly recommend the proper material type and configuration to meet your needs…and can quote your outage delivery requirements on a month basis.
Do you accept a special order?
A: Yes, we do. We can manufacture all kinds of chemical equipments according to your technical drawings(Before you givethem to us, will sign the contract and confidentiality agreement with you. You don’t need to worry about that.)
Can you make a design for us?
A: Yes, we can. What we supply is not only product, but also solution and design. And if you make the product in our factory,the design will be free. If not, design fees will be charged accordingly.
Q: Do you provide after-sales service?
A: Yes, we do. This product is guaranteed up to one year from purchase unless manmade damage. If there is anything wrongwith product itself quality problem,we will change or repair it at our charge.If not, we will provide aftersales service at your charge.

Tube erosion shields are mainly used on the windward side of the heating surface of the boiler, such as superheaters, reheaters, economizers, and water-cooled wall pipes.
Erosion shields are used to protect boiler tubing from the highly erosive effects of high temperatures and pressures thereby greatly extending tube life.
We offer shielding for tubing, covering straight, bent and finned sections, as well as the clips that hold these in place.
In the long term, these shields more than pay for themselves, preventing the costly replacement of tubing and avoiding the downtime that results from tube breakdown and leaks.
In general, most of them are called “wear-resistant tile” and “wear-resistant cover plate”. Erosion Shields are special boiler accessories.
Generally, most of them are used in power station boilers, small boilers are used less, and some coal chemical industries will also use them.
The main role is to protect the heating surface of the boiler pipes, reduce pipeline wear, and increase the heating surface of the pipes.





Generally, boiler tubes erosion shields are also installed to prevent further wear of the tubes and cause serious consequences such as boiler explosion.
The main role is to protect the heating surface of the boiler pipes, reduce pipeline wear, and increase the heating surface of the pipes.
The snap ring is a short section that is installed on the pipe in conjunction with the wear-resistant tile. Generally, it is welded to the wear-resistant tile by lap welding, that is, to cover the wear-resistant tile slightly, so it is larger than the wear-resistant tile. The opening arc is around 190-200 degrees, the welding position needs to be set aside to facilitate welding and fixing. The width of the snap ring must not be less than 20mm.
The installation requirements of anti-friction tiles of different shapes are slightly different. Basically, each anti-friction tile is installed with not less than 2-4 snap rings. The snap ring and the anti-friction tile are welded together to prevent expansion due to heat. The tiles fall off, and the joints are required to be fully welded.
Generally, boiler tubes erosion shields are also installed to prevent further wear of the tubes and cause serious consequences such as boiler explosion.
The main role is to protect the heating surface of the boiler pipes, reduce pipeline wear, and increase the heating surface of the pipes.

When you partner with Sunny Steel, you can stop worrying about meeting deadlines thanks to our responsive and timely service. You'll also say goodbye to unnecessary shopping around. Instead, you'll get white glove service from an expert who understands your needs and can get you the materials you need quickly.
