Erosion Shields
Erosion Shields are designed to eliminate major maintenance and downtime costs from boiler and condenser tube failure.
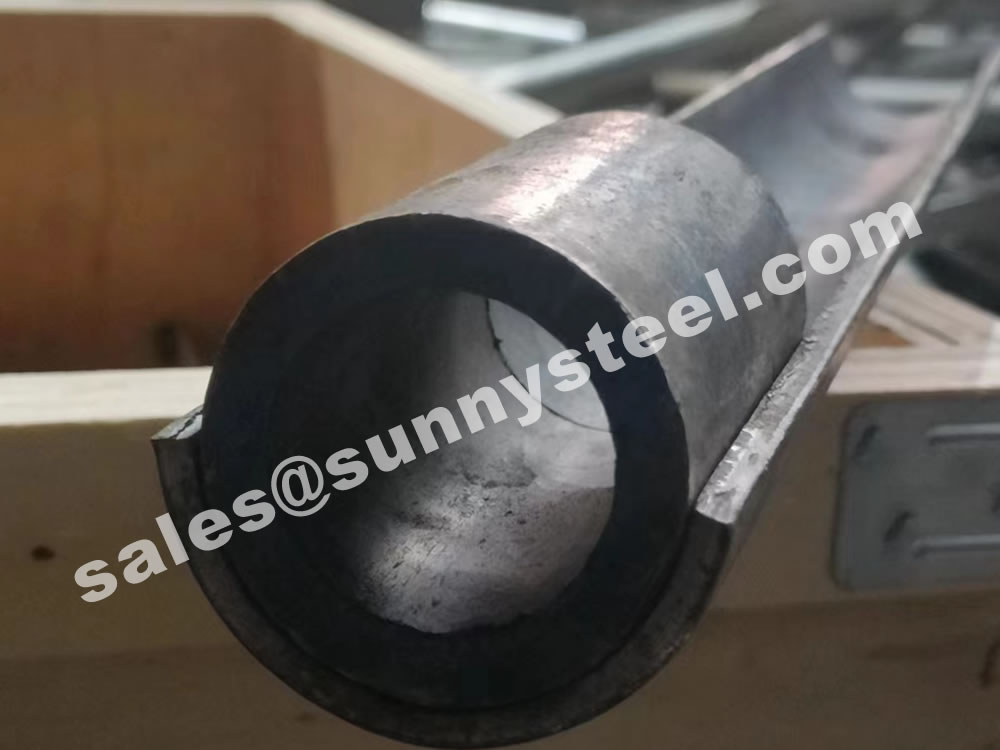

Q235 tube shield combines the advantageous properties of Q235 steel with the protective function of a tube shield, making it a reliable choice for safeguarding pipelines and tubes in industrial settings.
Discover the superior protection of Q235 Tube Shield. Durable and versatile, our steel tube shield ensures optimal performance, solving challenges and boosting efficiency in various applications.
Download PDFQ235 Tube Shields are protective covers that use Q235 carbon steel, known for its cost-effectiveness, strength, and flexibility. They are applied to the surface of pipes and tubes to prevent erosion, corrosion, and mechanical wear. The shield’s composition makes it suitable for various industrial applications where equipment is exposed to harsh conditions.
Q235 is a mild or low-carbon steel with a carbon content typically between 0.12% and 0.20%, which provides a balance of strength, ductility, and weldability. This steel is known for its ease of machining and forming, which contributes to its wide range of applications. Q235 is part of the GB/T 700 standard, used widely in China for structural steel products.
| Chemical Composition | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade | C | Mn | Si | S | P |
| Q235A | ≤0.22% | ≤1.4% | ≤0.35% | ≤0.050 | ≤0.045 |
| Q235B | ≤0.20% | ≤1.4% | ≤0.35% | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 |
| Q235C | ≤0.17% | ≤1.4% | ≤0.35% | ≤0.040 | ≤0.040 |
| Q235D | ≤0.17% | ≤1.4% | ≤0.35% | ≤0.035 | ≤0.035 |
Q235 is divided into four levels: A, B, C, D
Q235A/Q235B belongs to ordinary low-carbon steel, and Q235C/Q235D belongs to high-quality low-carbon steel.
| Mechanical Properties | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Grade | Yield Strength | Tensile Strength | Elongation % |
| Q235 Steel | 235 Mpa | 370-500 Mpa | 26 |
Q represents the yield limit of this material, and the subsequent 235 refers to the yield value of this material, which is approximately 235 MPa. Moreover, its yield value will decrease as the thickness of the material increases.
The impact toughness test uses Charpy ∨-shaped notched specimens. The impact toughness index is AKV.
For the above-mentioned grades B, C, and D steels, they are required to reach AKV≥27J under their respective temperature requirements. Therefore, the four ranks are ranked as A
Introducing Q235 Tube Shield, your ultimate solution for reliable tube protection. Crafted with precision using Q235 steel, our tube shield stands out in durability and versatility. Explore how this innovative shield addresses challenges, ensuring efficient performance in diverse scenarios.
235 belongs to low-carbon structural steel with a carbon content of about 0.12%-0.2%, which is equivalent to ordinary 10 and 20 steel. The hardness does not change much after quenching.
Q235 is generally bought without heat treatment. Generally, it is used in places where a large amount of steel is needed in engineering. The quantity is huge. Generally, it is used after hot rolling. Hot rolling is also a heat treatment of normalizing.
There are several reasons for not heat treatment
Q235, SS400, and ASTM A36 are carbon structural steel grades from Chinese, Japanese, and American standards, respectively. They share similarities in chemical composition and mechanical properties, making them comparable for various applications.
| Property | Q235 | SS400 | ASTM A36 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition (%) | |||
| Carbon (C) | ≤ 0.22 | ≤ 0.20 | ≤ 0.26 |
| Silicon (Si) | ≤ 0.35 | ≤ 0.35 | ≤ 0.40 |
| Manganese (Mn) | ≤ 1.40 | ≤ 1.40 | 0.60–1.20 |
| Sulfur (S) | ≤ 0.050 | ≤ 0.050 | ≤ 0.050 |
| Phosphorus (P) | ≤ 0.045 | ≤ 0.050 | ≤ 0.040 |
| Mechanical Properties | |||
| Yield Strength (MPa) | ≥ 235 | ≥ 245 | ≥ 250 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 370–500 | 400–510 | 400–550 |
While all three grades are used in structural applications due to their weldability and formability, there are slight differences in their mechanical properties. ASTM A36 and SS400 have marginally higher yield and tensile strengths compared to Q235. However, in practical applications, these materials are often considered interchangeable, depending on specific project requirements and regional availability.
The distinction between low-carbon steel and high-carbon steel lies in the carbon content and hardness. High-carbon steel is often referred to as tool steel, with the carbon content ranging from 0.60% to 1.70%, and it can be quenched and tempered.
Low-carbon steel is a type of carbon steel with a carbon content of less than 0.25%. Due to its low strength, low hardness, and softness, it is also known as mild steel.
The simplest and most direct way to ascertain the carbon content of carbon steel is to grind sparks on the grinding wheel.
The differences in sparks: The sparks of low-carbon steel are linear and rarely branched; the sparks of medium-carbon steel have more points and forks; the sparks of high-carbon steel branch a lot; there are also differences in brightness – the higher the carbon content, the brighter.
Q235 Tube Shield finds wide applications in industrial pipelines, construction sites, and more. Its flexibility and versatility make it the ideal choice for pipeline protection in various industries. Whether in harsh environments or for long-term pipeline preservation, Q235 Tube Shield showcases exceptional performance.
Due to its favorable properties and cost-effectiveness, Q235 steel is used in various applications:
Q235 steel is a type of low-carbon steel, manufactured according to the GB/T700 standard of China.
It is divided into four grades: Q235A, Q235B, Q235C, and Q235D. With a density of 7.85g/cm3, Q235 steel has a tensile strength ranging from 370 to 500 MPa and a compressive strength of 235 MPa (for steel bars or plates with a thickness of 16mm). With an appropriate carbon content in Q235 steel, this type of steel often exhibits good overall performance and a good balance of strength, flexibility, and weldability. It is produced in various forms such as plates, round bars, square bars, flat bars, angles, channels, I-beams, and steel pipes, serving industries such as construction, bridges, ships, and vehicles. Q235 steel is widely used in construction and engineering industries, from making steel bars for workshop structures and high-voltage transmission towers to use in boiler manufacturing, containers, and many other mechanical applications requiring stable operational performance.
The characteristics of Q235 steel are determined by several important factors:
Not only does Q235 possess toughness, weldability, and excellent plasticity, but it also retains strength while offering outstanding cold-bending performance. It is perfect for welded structures, including factory buildings, steel bars, towers, boilers, bridges, containers, vehicles, and more. Q235 can also be used as mechanical parts, such as stands, stressed rods, nuts, connecting rods, brackets, and other components. Q235 and varying grades of steel plates can be cut to specification.
As the thickness of the material increases, the yield value of Q235 decreases. Due to its moderate carbon content, the performance is comprehensive and adequate. Q235 also matches well in strength, welding, and plasticity. Most often, it is rolled into a steel plate, rod, bar, or angle frame. It is most commonly used in the engineering and construction industries.
The Q235 steel material is in accordance with PRC standards. Carbon steel for special projects and purposes, like marine and bridge steel, typically uses carbon structural steel expression. However, the letter indicating intents and purposes is included at the end of the steel grade.
While the Q235 grade steel plate has lower mechanical properties than the A36 materials, these materials can generally be substituted for one another, as long as there are no special requirements and needs involved. If only considering the material’s mechanical properties, it is generally acknowledged that Q235 and A36 are similar to those of high-quality carbon structural steel.
The Q235 steel can be substituted with equivalent materials that include A36 (USA ASTM), Q235 (China GB/T), and SS400 (Vietnam/Japanese JIS), S275(European standard).
Not only does Q235 possess toughness, weldability, and excellent plasticity, it retains strength while offering outstanding cold-bending performance. It is perfect for welded structures, such as factory buildings, steel bars, towers, boilers, bridges, containers, vehicles, and more. Q235 can also be used as mechanical parts, such as stands, stressed rods, nuts, connecting rods, brackets, and other components. Q235 and varying grades of steel plates can be cut to specification.
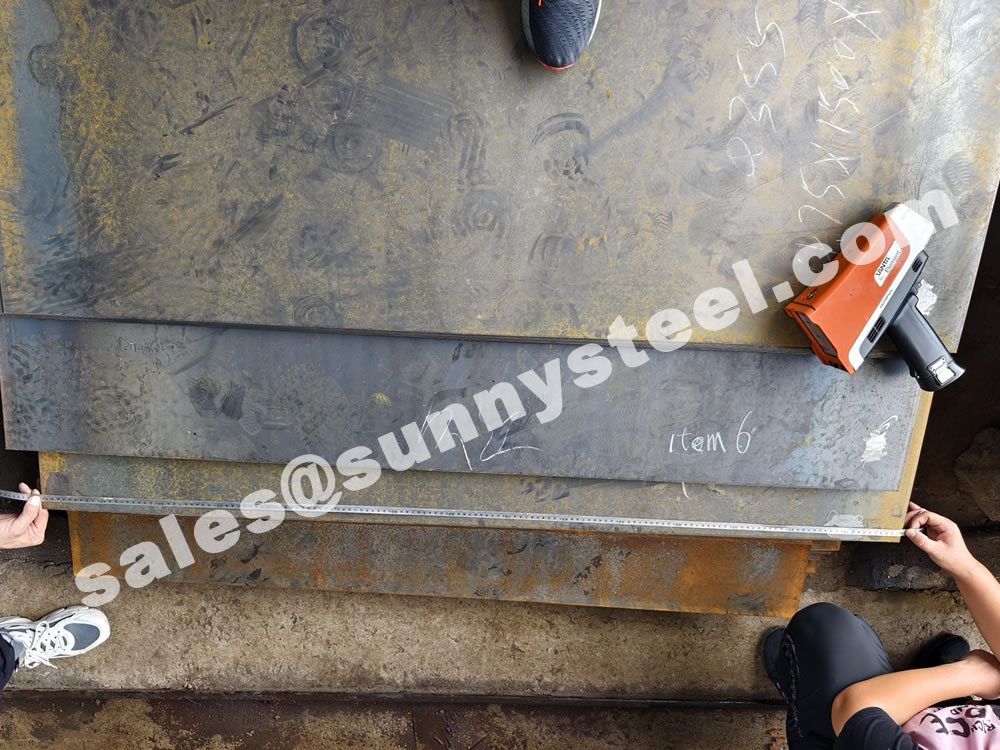
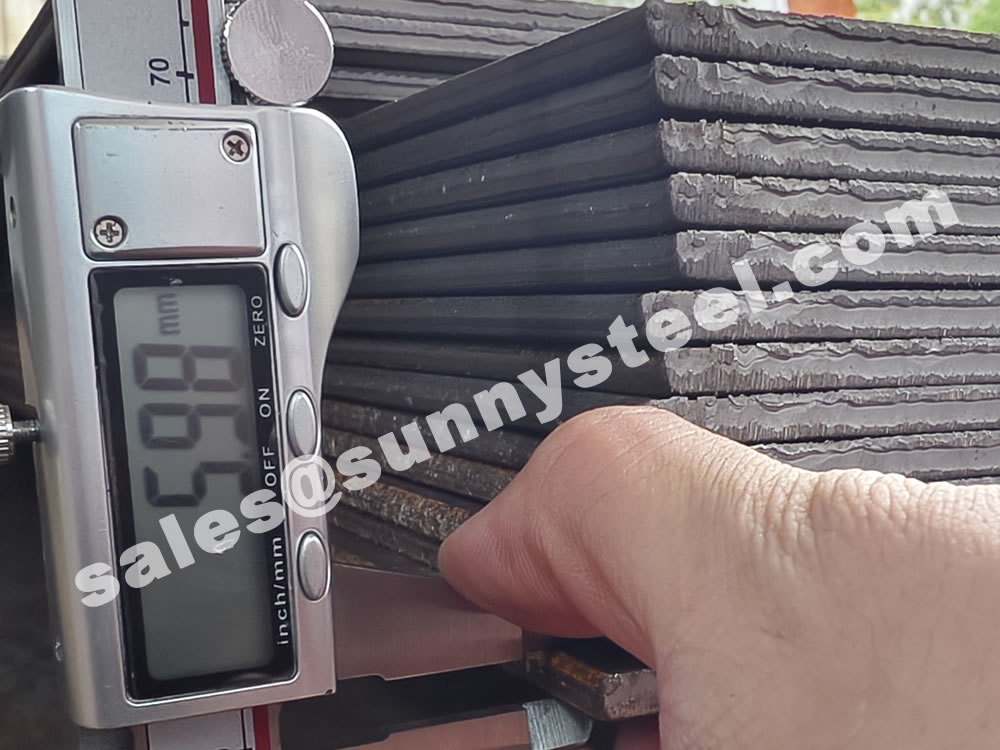
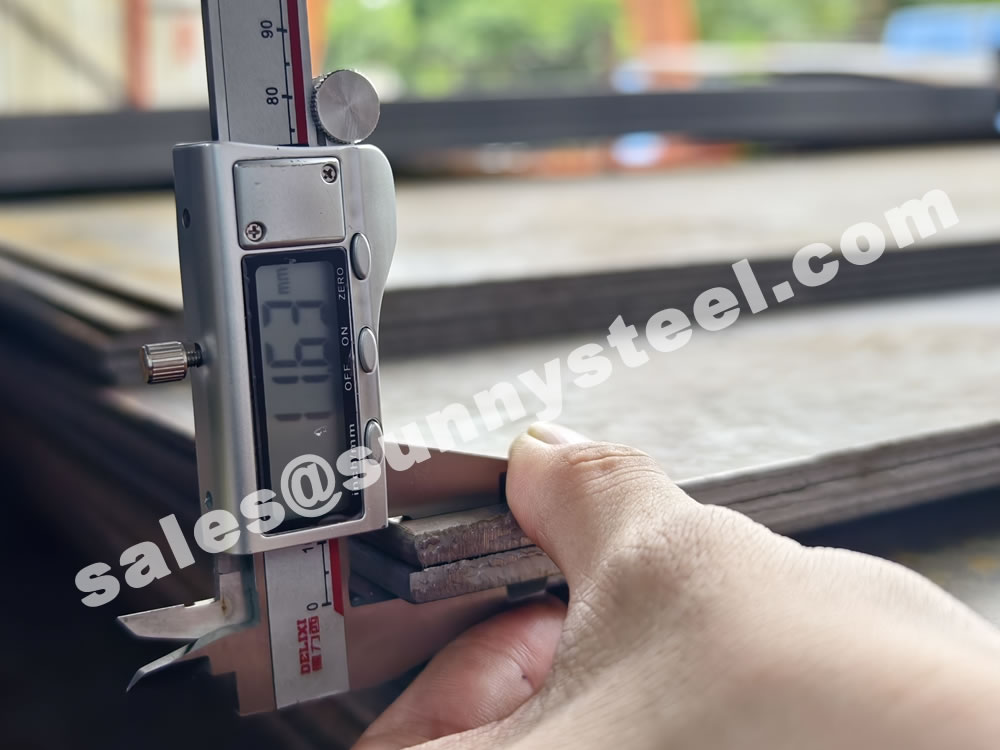
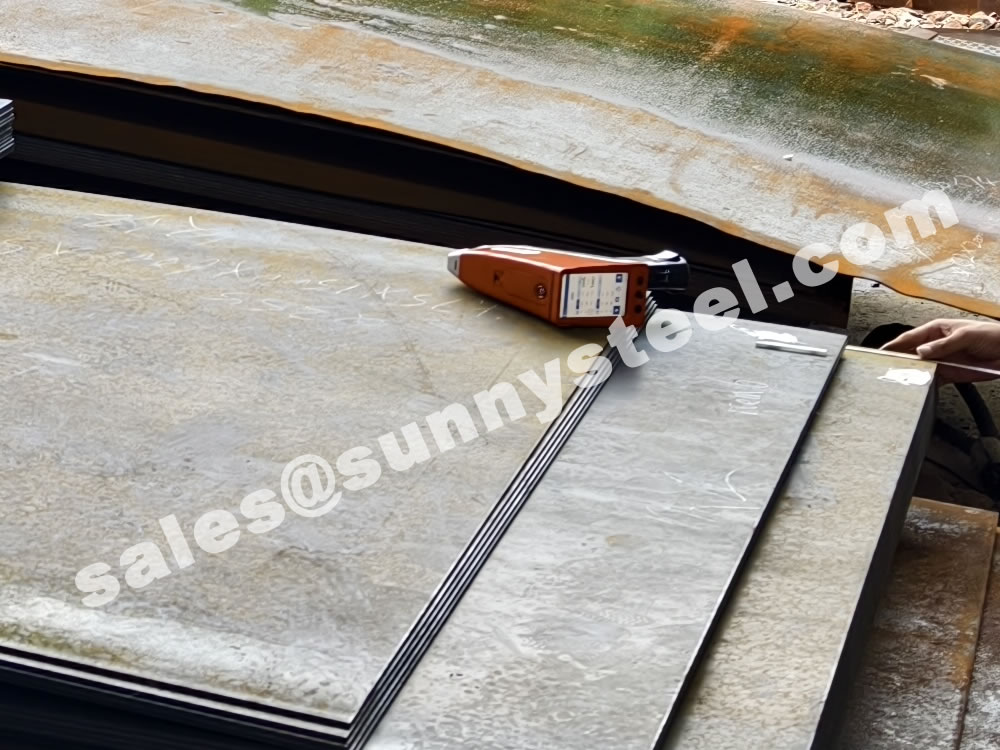
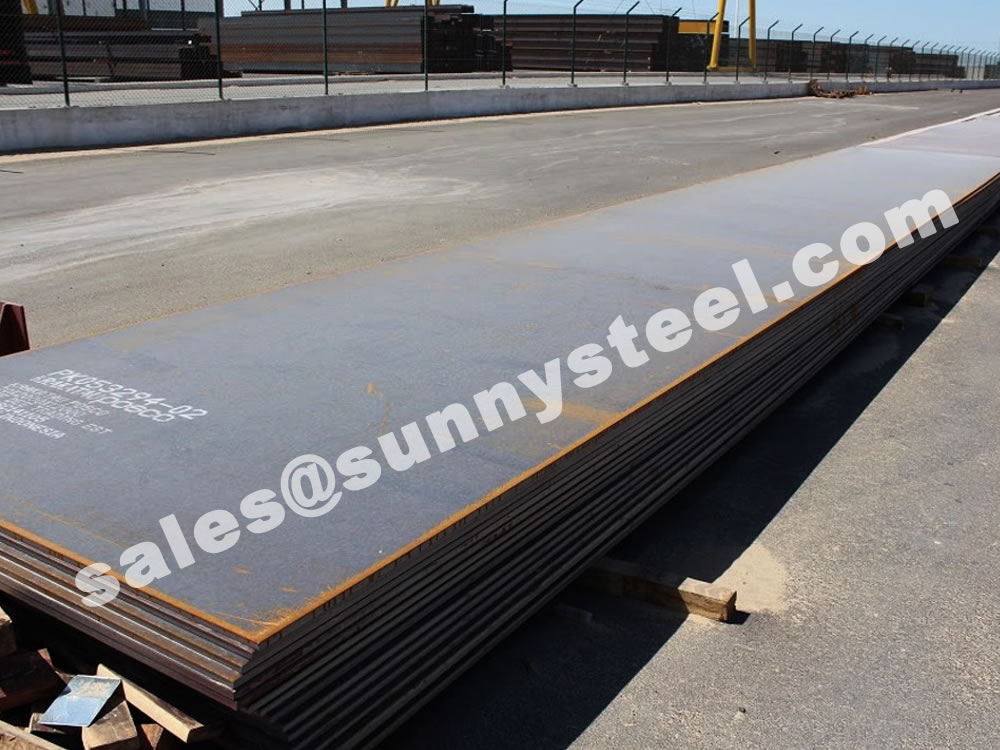
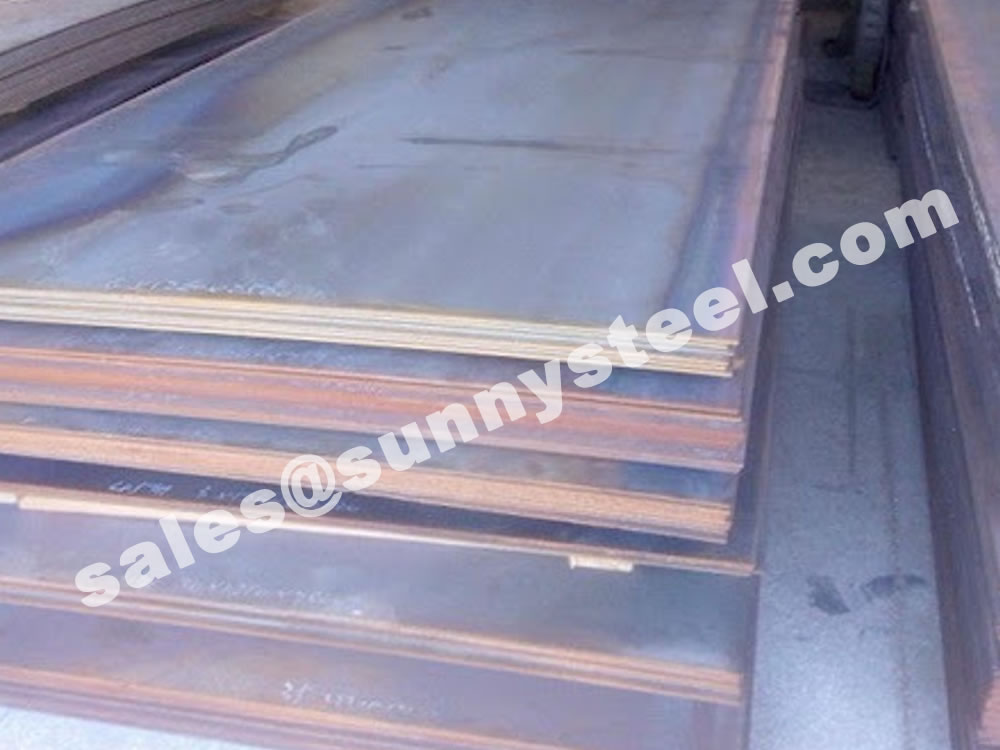









Q235 steel plate is highly regarded for its outstanding advantages:
These advantages make Q235 steel plate a popular and preferred choice in many applications, from infrastructure to manufacturing and construction.
The cross-sectional shape of boiler tubes shields is mostly semi-circular (180 degrees), and there are also 120-160 degrees.
It is mainly used on finned tubes (water-cooled walls); boiler tube erosion shields are divided into direct wear-resistant shields, in-curve, anti-wear shields, outer-curve, anti-wear shields, side-curve anti-wear shields, s-curve anti-wear shields, etc.
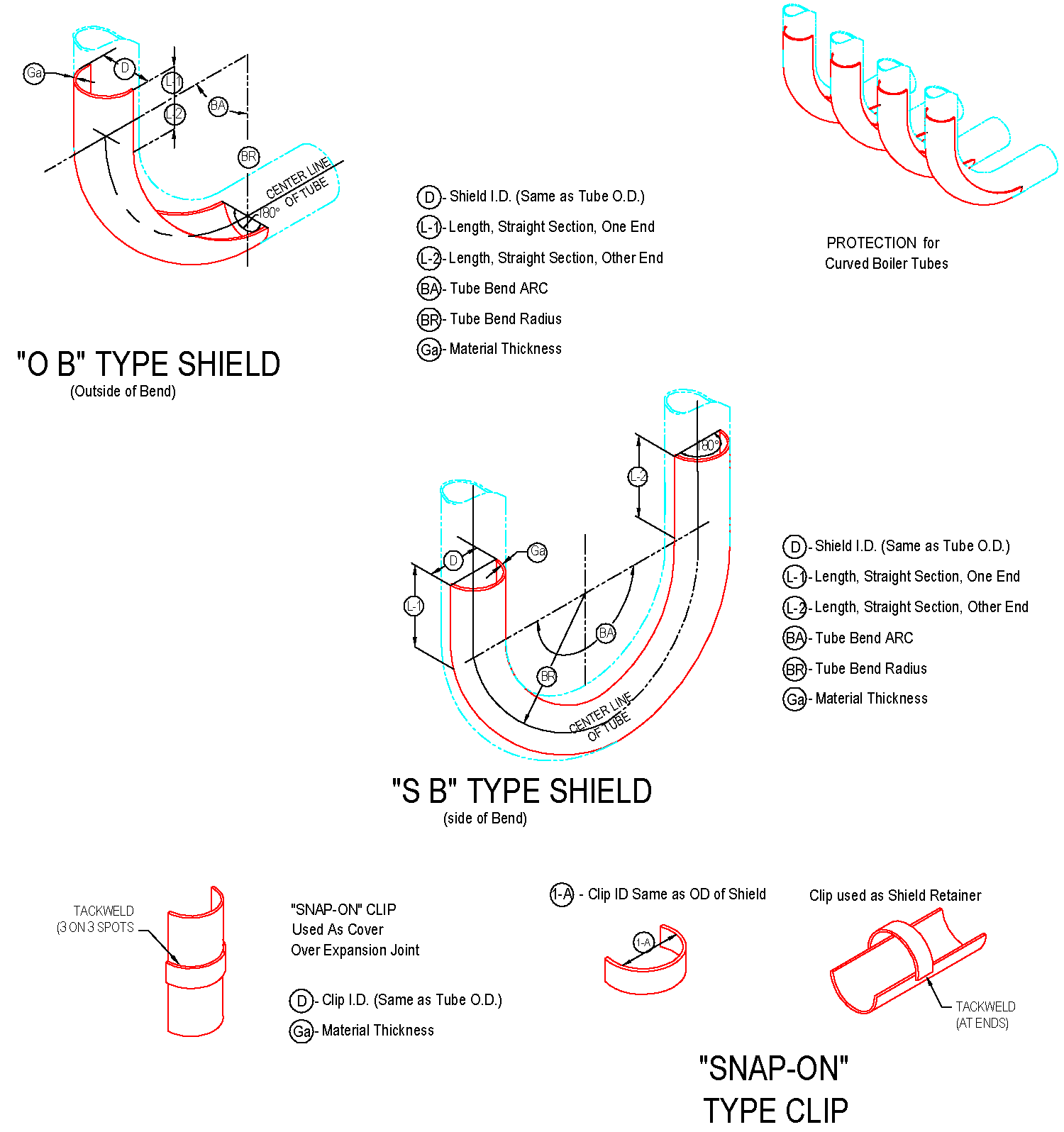
The length of the straight anti-wear shields ranges from 20mm to 3000mm, and the general length of 1000-2000mm is commonly used. The anti-wear shields with bends generally requires a processing drawing and the following parameters should be on the drawing: outer diameter of the pipe used, bending of the pipe Radius R (to the center of the pipe), the degree of bending angle, and the length of the straight sections on both sides of the arc segment of the wear-resistant shields.
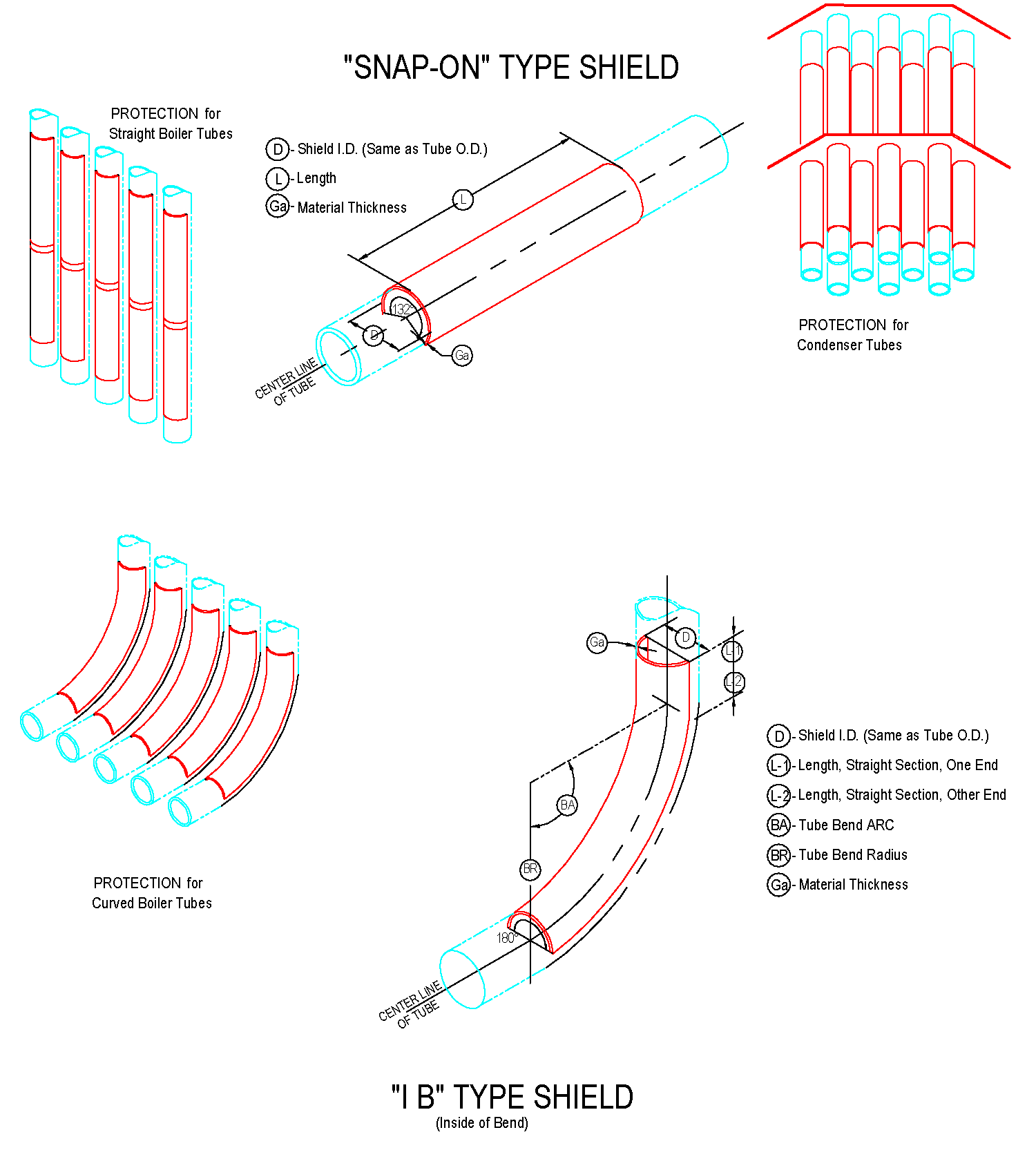
The most basic parameter of boiler tubes shields is the outer diameter of the tube used (that is, the inner diameter of boiler tubes erosion shields). The main specifications of the tube are: 32, 38, 42, 44.5, 48, 51, 57, 60, 63.5 , 76, 89mm, etc . the inner diameter of the boiler tubes erosion shields is usually 1-3mm larger than the outer diameter of the tube used, depending on the actual requirements.
The current production process for tube shields is to use high-pressure presses and professional moulds for pressing.
Tube shields from us are manufactured to exacting standards. Advanced equipment and material handling capabilities permit us to offer the fastest turnaround times anywhere.
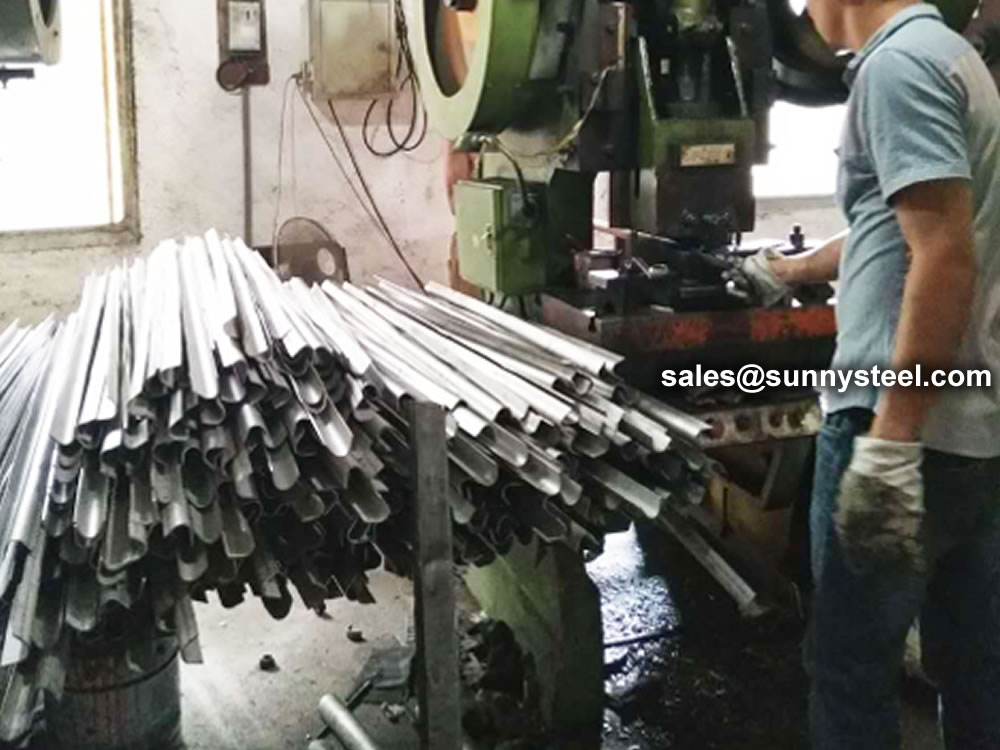

The current production process for tube shields is to use high-pressure presses and professional moulds for pressing.
The production time is short, the welding performance is good, the welding seam does not fall off, the surface is smooth and the appearance is beautiful. The arc-shaped wear-resistant tile is pressed on a press or bent on a pipe bender with a special mould.

To ensure the accuracy of the material. Positive Material Identification (PMI) of stainless steel sheets for tube shields is critical to verifying the grade and composition of stainless steel before it goes into production.
The raw materials for the production of tube shields are generally purchased directly from standard steel mills, and each batch has an MTC. Due to the sharpe limitations of raw materials, it is inevitable that excess materials will be produced. We can use the excess material to make a smaller size snap ring.
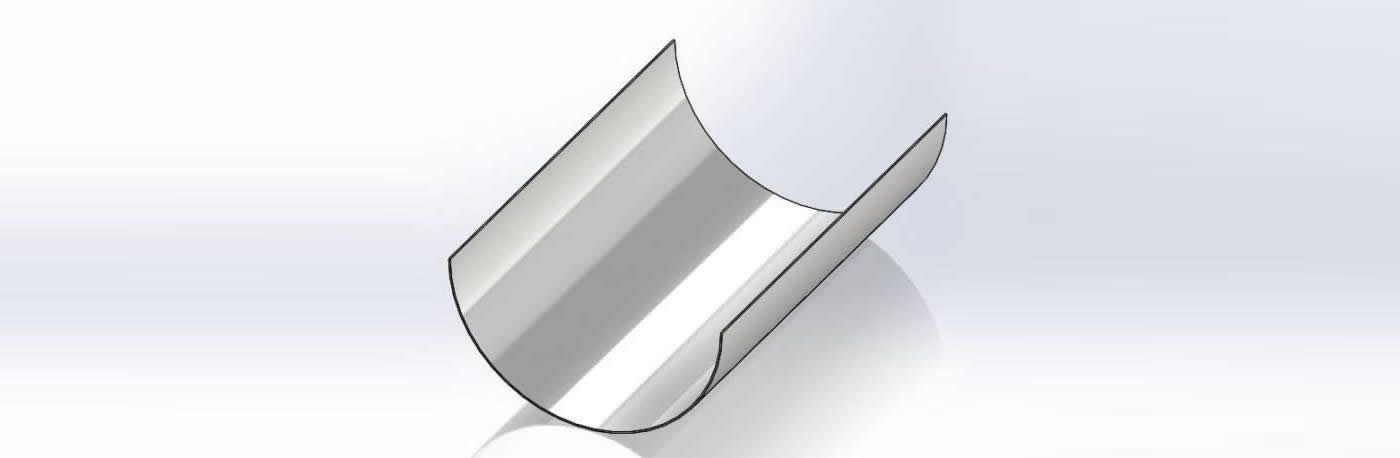
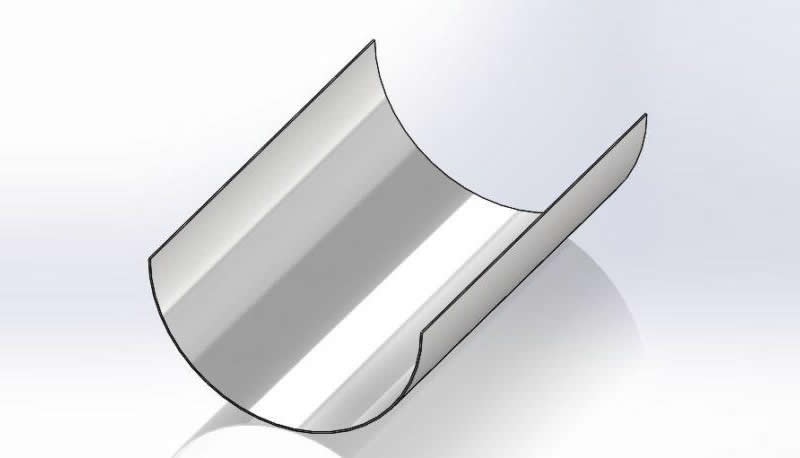
Different types of stainless steel are selected according to the specific conditions of different working conditions.
The boiler was originally designed to be accurate. Different materials have different temperature resistance and mechanical strength, generally has a temperature resistance of 600 ℃ or less.
We can also supply boiler tubes erosion shields of other materials.

Tube shields are custom made to fit perfectly to straight sections, curved sections and even finned and specialised tubing.
Boiler tube erosion shields, also known as anti-corrosion shields, anti-wear plate, anti-wear protection shields, anti-wear cover plate, anti-corrosion cover plate, boiler climbing pipe, anti-wear pressure plate, etc. , which are used in combination with snap rings.
Boiler tube erosion shields are produced using a high-pressure press and professional mould pressing. The production time is short, the welding performance is good, the welding should not fall off, the surface is smooth, and the appearance is beautiful. Boiler tube erosion shields with bends are formed by pressing on a press or bending with a special abrasive on a tube bender.
Boiler tube shields are designed to eliminate major maintenance and downtime costs from boiler and condenser tube failure.
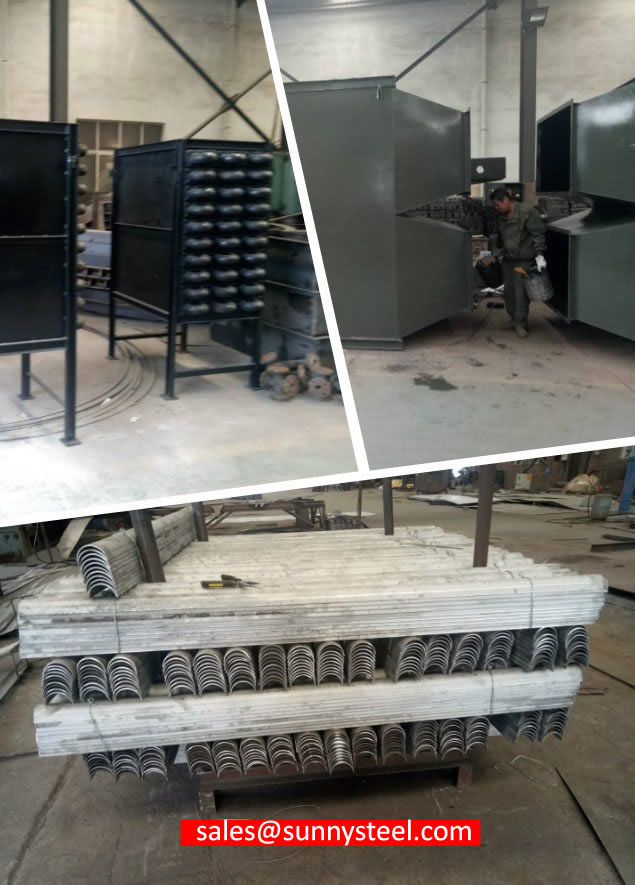

The service life of boiler tubes erosion shields is different in different types of boilers and different use parts.
The normal service life is a period of overhaul (3-5 years) for the boiler. Generally, some boilers will be replaced or retrofitted every time the boiler is overhauled. The main replacements are those of the Boiler Tubes Erosion Shields that are severely thinned and exceeded the standard; those that were not firmly detached during the boiler operation during the previous installation. According to the wear of the Boiler Tubes Erosion Shields during replacement, if the thickness is severely reduced, it needs to be replaced, the deformation is severe, and those that cannot protect the tube also need to be replaced. In addition, some boiler tubes are not equipped with Boiler Tubes Erosion Shields, but during the boiler inspection, it is found that the tubes have a tendency of wear and thinning. Generally, Boiler Tubes Erosion Shields are also installed to prevent further wear of the tubes and cause serious consequences such as boiler explosion.
On the heating surface of superheater and economizer tube bundle of the boiler, in order to prevent the pipe from being worn by high temperature flue gas washing, boiler tubes erosion shields are mostly arranged on the outer side of the pipe in the direction of flue gas flow. The elbow erosion shields solves the abrasion problems of water wall tubes, superheater tubes, economizer tubes and reheater tubes in the furnace, and provides guarantee for the long-term and reliable operation of CFB boiler. With the increase of CFB boiler products, the type and quantity of The elbow erosion shields will increase.
Our understanding of and commitment to the steam and power generation business enables us to solve your boiler tube erosion or corrosion problems efficiently. Our technical staff can quickly recommend the proper material type and configuration to meet your needs…and can quote your outage delivery requirements on a month basis.
Do you accept a special order?
A: Yes, we do. We can manufacture all kinds of chemical equipments according to your technical drawings(Before you givethem to us, will sign the contract and confidentiality agreement with you. You don’t need to worry about that.)
Can you make a design for us?
A: Yes, we can. What we supply is not only product, but also solution and design. And if you make the product in our factory,the design will be free. If not, design fees will be charged accordingly.
Q: Do you provide after-sales service?
A: Yes, we do. This product is guaranteed up to one year from purchase unless manmade damage. If there is anything wrongwith product itself quality problem,we will change or repair it at our charge.If not, we will provide aftersales service at your charge.

Tube erosion shields are mainly used on the windward side of the heating surface of the boiler, such as superheaters, reheaters, economizers, and water-cooled wall pipes.
Erosion shields are used to protect boiler tubing from the highly erosive effects of high temperatures and pressures thereby greatly extending tube life.
We offer shielding for tubing, covering straight, bent and finned sections, as well as the clips that hold these in place.
In the long term, these shields more than pay for themselves, preventing the costly replacement of tubing and avoiding the downtime that results from tube breakdown and leaks.
In general, most of them are called “wear-resistant tile” and “wear-resistant cover plate”. Erosion Shields are special boiler accessories.
Generally, most of them are used in power station boilers, small boilers are used less, and some coal chemical industries will also use them.
The main role is to protect the heating surface of the boiler pipes, reduce pipeline wear, and increase the heating surface of the pipes.





Generally, boiler tubes erosion shields are also installed to prevent further wear of the tubes and cause serious consequences such as boiler explosion.
The main role is to protect the heating surface of the boiler pipes, reduce pipeline wear, and increase the heating surface of the pipes.
The snap ring is a short section that is installed on the pipe in conjunction with the wear-resistant tile. Generally, it is welded to the wear-resistant tile by lap welding, that is, to cover the wear-resistant tile slightly, so it is larger than the wear-resistant tile. The opening arc is around 190-200 degrees, the welding position needs to be set aside to facilitate welding and fixing. The width of the snap ring must not be less than 20mm.
The installation requirements of anti-friction tiles of different shapes are slightly different. Basically, each anti-friction tile is installed with not less than 2-4 snap rings. The snap ring and the anti-friction tile are welded together to prevent expansion due to heat. The tiles fall off, and the joints are required to be fully welded.
Generally, boiler tubes erosion shields are also installed to prevent further wear of the tubes and cause serious consequences such as boiler explosion.
The main role is to protect the heating surface of the boiler pipes, reduce pipeline wear, and increase the heating surface of the pipes.

When you partner with Sunny Steel, you can stop worrying about meeting deadlines thanks to our responsive and timely service. You'll also say goodbye to unnecessary shopping around. Instead, you'll get white glove service from an expert who understands your needs and can get you the materials you need quickly.
