
Austenitic Stainless Flanges For Boiler Pipe Safeguarding And Oxidation Resistance In Industrial Piping Systems
Astm a182 ss 310/310s flanges deliver exceptional corrosion resistance and erosion protection for high-temperature pipelines and boilers.
Austenitic Stainless Flanges For Boiler Pipe Safeguarding And Oxidation Resistance In Industrial Piping Systems
Astm a182 ss 310/310s flanges deliver exceptional corrosion resistance and erosion protection for high-temperature pipelines and boilers.
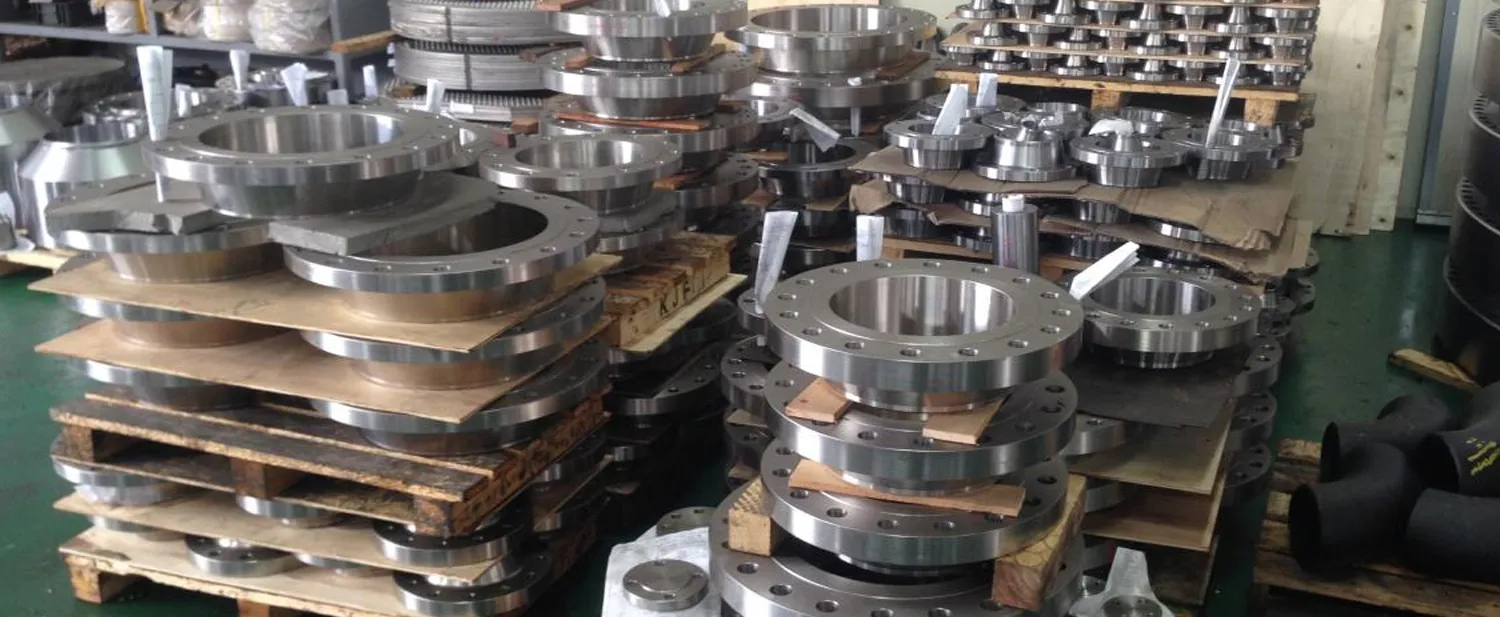


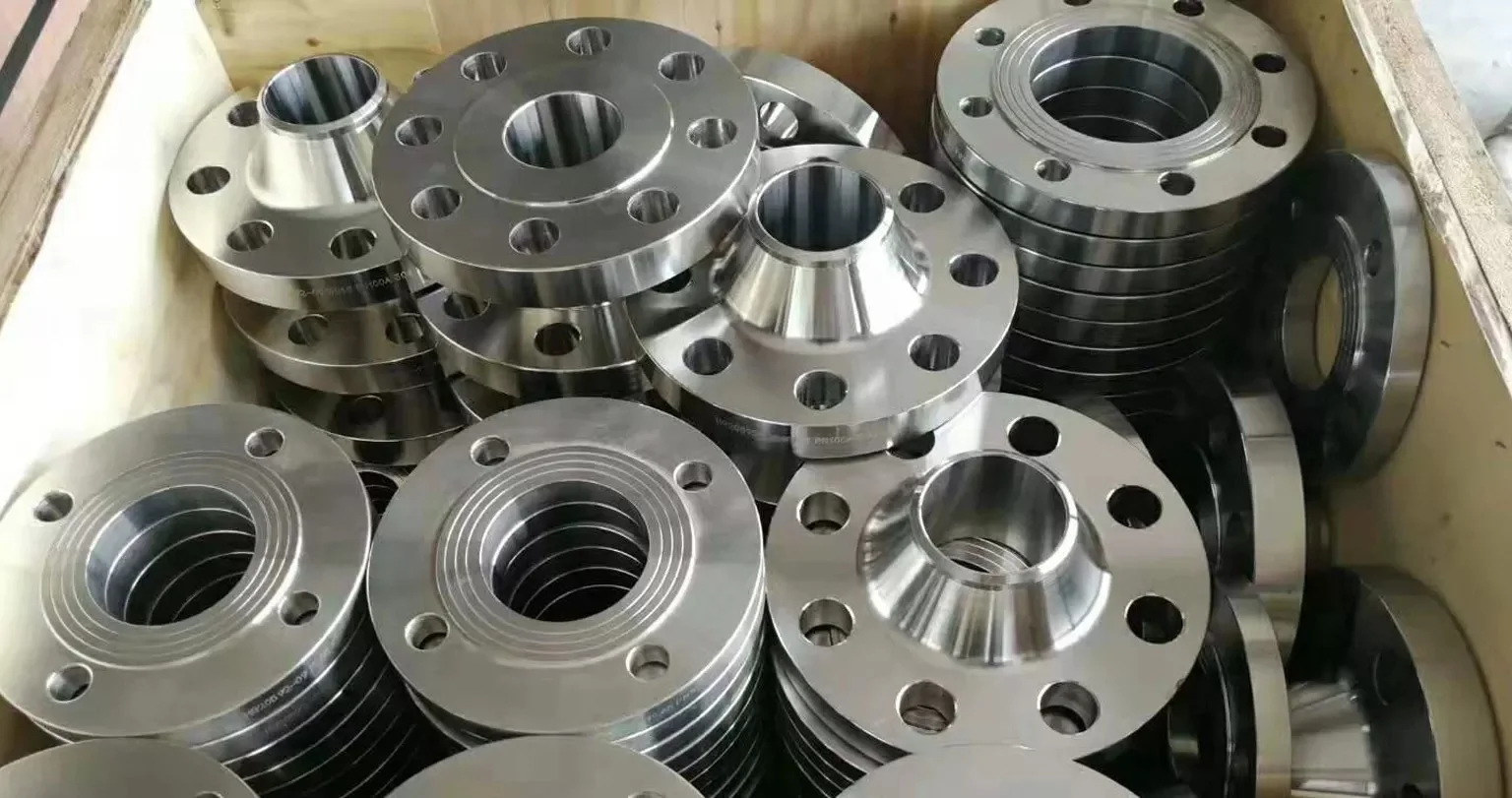
ASTM A182 SS 310/310S Flanges stand out as premium forged components engineered for the most demanding high-temperature and corrosive applications, providing robust boiler pipe protection and pipeline corrosion protection in industries like petrochemicals, power generation, and furnaces. Composed of austenitic stainless steels—SS 310 (UNS S31000) for superior high-temperature strength and SS 310S (UNS S31008) with low carbon for enhanced weldability—these flanges offer unmatched resistance to oxidation, carburization, and pitting, making them essential for erosion resistance flanges in environments exposed to extreme heat up to 1100°C and aggressive media like acids, alkalis, and chlorides.
The hallmark of these corrosion resistant flanges is their ability to maintain structural integrity under thermal cycling and high-velocity flows, directly addressing common challenges such as boiler pipe grinding, thermal fatigue, and chemical-induced degradation. For instance, in furnace piping systems, SS 310/310S flanges form leak-proof connections that prevent costly failures from abrasive slurries or hot gases, aligning perfectly with user searches for "industrial pipeline protection solutions" or "boiler corrosion resistant fittings." Their high creep strength and non-magnetic properties further enhance formability and longevity, reducing maintenance frequency and operational costs in refineries, heat exchangers, and steam circuits.
Compliant with global standards including ASTM A182/ASME SA182 for material forging, ANSI/ASME B16.5 for dimensions, and EN-1092 for pressure ratings, these high-temperature flanges are available in a wide array of configurations to suit diverse needs. Sizes span from 1/2" (15 NB) to 48" (1200 NB), with pressure classes from ANSI 150# to 2500# and PN6 to PN64, ensuring seamless integration into existing setups. Popular types include Weld Neck Flanges for high-pressure integrity, Slip-On Flanges for economical assembly, Blind Flanges for temporary sealing during pressure tests, Threaded Flanges for quick installations, and Ring Type Joint (RTJ) Flanges for extreme sealing demands. Face options like Raised Face (RF) for optimal gasket compression or Tongue-and-Groove (T&G) for anti-erosion flow control add versatility, while custom finishes minimize particle impingement in erosion-prone pipelines.
Mechanically, these flanges boast a tensile strength of 515 MPa, yield strength of 205 MPa, and 40% elongation, coupled with a density of 7.9 g/cm³ and melting point of 1402°C, guaranteeing durability without brittleness. The chemical makeup—featuring 24-26% chromium for oxidation barriers and 19-22% nickel for thermal stability—positions them as a go-to for long-tail queries like "ASTM A182 310S flanges for boiler erosion resistance" or "SS 310 corrosion resistant pipeline flanges PN16." In power plants, they excel at safeguarding exhaust lines against flue gas corrosion; in chemical reactors, they resist nitriding and carburization; and in oil & gas, they combat hydrogen-induced cracking.
Beyond core specs, ASTM A182 SS 310/310S flanges solve real-world pain points by offering 100% radiography, ultrasonic testing, and PMI certification options, ensuring traceability and compliance. Paired with complementary gaskets or bolts, they form complete assemblies that boost system efficiency. As a Mumbai-based manufacturer, OMA Alloy Forgings provides ready stock for exports to over 50 countries, including fast delivery for urgent projects. For engineers tackling "boiler pipeline wear solutions," these flanges deliver proactive defense: fewer leaks, extended lifespans, and lower total ownership costs. Explore dimensional charts or request quotes for tailored erosion resistance flanges today.
| Aspect | SS 310/310S Advantage | Application Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Oxidation Resistance | Up to 1100°C without scaling | Prevents boiler pipe degradation in furnaces |
| Weldability (310S) | Low C minimizes sensitization | Seamless integration for pipeline anti-corrosion |
| Creep Strength | High under prolonged heat | Reduces thermal fatigue in power plant piping |
| Erosion Mitigation | Robust forging & smooth faces | Ideal for high-velocity slurry transport |
A stainless steel flange (SS flange) is a key piping component designed for strength, corrosion resistance, and durability across industries.
Stainless steel flanges are vital components in various industrial processes, serving as connectors or joint pieces between pipes, valves and other equipment. Made from a blend of iron, chromium and nickel, stainless steel flanges boast exceptional strength and resistance to corrosion, making them suitable for use in harsh environments. These versatile flanges come in different shapes and sizes to suit the diverse needs of industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, water treatment, etc. They also offer excellent sealing capabilities to prevent leakages and ensure a safe working environment. Stainless steel flanges are available in various shapes, sizes, and grades to meet specific application requirements.
A stainless steel flange is used to connect pipes, valves, pumps, and other equipment in piping systems. Common material standards and grades include ASTM A182 Grade F304/L and F316/L, with pressure ratings from Class 150 to Class 2500.
Compared to carbon steel flanges, stainless steel flanges offer superior corrosion resistance, longer service life, and a clean, professional appearance.
Excellent performance in harsh and corrosive environments.
Suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature service.
Clean surface finish, ideal for hygienic industries.
Widely used in oil & gas, chemical, food, marine, and power industries.
| Grade | Main Feature | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 304 | General purpose, good corrosion resistance | Water, gas, low-temp service |
| 304L | Low carbon, improved weldability | Welded piping systems |
| 316 | Superior resistance to chlorides & acids | Marine, chemical, offshore |
| 316L | Low carbon, excellent corrosion resistance | High corrosive welded environments |
| 321 | Titanium stabilized, high-temp strength | Heat exchangers, aerospace, boilers |
| Product Category | Flange Types | Key Details |
|---|---|---|
| General Specifications | ||
| Size Range | Tube: 25.4mm - 152.4mm | Pipe: 15NB - 250NB | |
| Material Grade | Grade 316 Stainless Steel (for Table D SOW) | |
| Table D Series | ||
| Table D | Slip on Weld (SOW) Tube and Pipe | Slipped over round pipe, welded inside and outside |
| Table D | Blind | - |
| Table E Series | ||
| Table E | Slip on Weld (SOW) Tube and Pipe | - |
| Table E | Blind | - |
| Table E | BSP Threaded | - |
| ANSI Series (150lb) | ||
| ANSI 150lb | Slip on Weld (SOW) Tube | - |
| ANSI 150lb | Slip on Weld (SOW) Pipe | - |
| ANSI 150lb | Blind | - |
| ANSI 150lb | BSP Threaded | - |
| ANSI Series (300lb) | ||
| ANSI 300lb | Slip on Weld (SOW) Pipe | - |
| ANSI 300lb | Blind | - |
| DIN Series (PN16) | ||
| DIN PN16 | Slip on Weld (SOW) Tube and Pipe | - |
| DIN PN16 | Blind | - |

We stock stainless steels in a multitude of shapes and sizes.
We support our stainless steel stock with a wide range of shapes and sizes to suit your engineering applications. We hold thirteen different types of shapes to support the grades of material we stock, including bars, sheets and plates.
Stainless Carbon Steel Composite Pipe
Sort:99
Material-Specific Erosion Shields
Sort:99
| Grade | C (% max) | Mn (% max) | Si (% max) | P (% max) | S (% max) | Cr (%) | Ni (%) | Mo (%) | N (% max) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 | 0.08 | 2.00 | 1.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 18.0-20.0 | 8.0-11.0 | - | 0.10 |
| 304L | 0.03 | 2.00 | 1.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 18.0-20.0 | 8.0-12.0 | - | 0.10 |
| 316 | 0.08 | 2.00 | 1.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 16.0-18.0 | 10.0-14.0 | 2.0-3.0 | 0.10 |
| 316L | 0.03 | 2.00 | 1.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 16.0-18.0 | 10.0-14.0 | 2.0-3.0 | 0.10 |
The low carbon content in 304L and 316L enhances weldability, while molybdenum in 316 and 316L improves resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, making ASTM A182 SS 310/310S Flange ideal for harsh environments.
| Grade | Tensile Strength (min, MPa) | Yield Strength (min, MPa) | Elongation (min, %) | Hardness (max, HB) | Hardness (max, HRB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 | 515 | 205 | 40 | 201 | 92 |
| 304L | 485 | 170 | 40 | 201 | 92 |
| 316 | 515 | 205 | 40 | 217 | 95 |
| 316L | 485 | 170 | 40 | 217 | 95 |
These mechanical properties make ASTM A182 SS 310/310S Flange suitable for applications requiring high strength and corrosion resistance, such as architectural structures, marine environments, and chemical processing.
In order to solve the cumbersome and difficult to remember stainless steel grades, improve the practicability of the brand representation, and the contrast with the international standard grades, China has formulated the "Universal Code System for Steel and Alloy Grades", such as 06Cr19Ni10, corresponding to 304. Different grades of stainless steel have different ingredients, but they all have a national standard. The standards of each country are also different.
| No | China (GB) | Japan (JIS) | American | Korea (KS) | EU (BS EN) | India (IS) | Australia (AS) | Taiwan (CNS) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Old | New (07.10) | SUS | ASTM | UNS | STS | EN | IS | AS | CNS | |
| Austenitic Stainless Steel | ||||||||||
| 1 | 1Cr17Mn6Ni5N | 12Cr17Mn6Ni5N | SUS201 | 201 | S20100 | STS201 | 1.4372 | 10Cr17Mn6Ni4N20 | 201-2 | 201 |
| 2 | 1Cr18Mn8Ni5N | 12Cr18Mn9Ni5N | SUS202 | 202 | S20200 | STS202 | 1.4373 | — | — | 202 |
| 3 | 1Cr17Ni7 | 12Cr17Ni7 | SUS301 | 301 | S30100 | STS301 | 1.4319 | 10Cr17Ni7 | 301 | 301 |
| 4 | 0Cr18Ni9 | 06Cr19Ni10 | SUS304 | 304 | S30400 | STS304 | 1.4301 | 07Cr18Ni9 | 304 | 304 |
| 5 | 00Cr19Ni10 | 022Cr19Ni10 | SUS304L | 304L | S30403 | STS304L | 1.4306 | 02Cr18Ni11 | 304L | 304L |
| 6 | 0Cr19Ni9N | 06Cr19Ni10N | SUS304N1 | 304N | S30451 | STS304N1 | 1.4315 | — | 304N1 | 304N1 |
| 7 | 0Cr19Ni10NbN | 06Cr19Ni9NbN | SUS304N2 | XM21 | S30452 | STS304N2 | — | — | 304N2 | 304N2 |
| 8 | 00Cr18Ni10N | 022Cr19Ni10N | SUS304LN | 304LN | S30453 | STS304LN | — | — | 304LN | 304LN |
| 9 | 1Cr18Ni12 | 10Cr18Ni12 | SUS305 | 305 | S30500 | STS305 | 1.4303 | — | 305 | 305 |
| 10 | 0Cr23Ni13 | 06Cr23Ni13 | SUS309S | 309S | S30908 | STS309S | 1.4833 | — | 309S | 309S |
| 11 | 0Cr25Ni20 | 06Cr25Ni20 | SUS310S | 310S | S31008 | STS310S | 1.4845 | — | 310S | 310S |
| 12 | 0Cr17Ni12Mo2 | 06Cr17Ni12Mo2 | SUS316 | 316 | S31600 | STS316 | 1.4401 | 04Cr17Ni12Mo2 | 316 | 316 |
| 13 | 0Cr18Ni12Mo3Ti | 06Cr17Ni12Mo2Ti | SUS316Ti | 316Ti | S31635 | — | 1.4571 | 04Cr17Ni12MoTi20 | 316Ti | 316Ti |
| 14 | 00Cr17Ni14Mo2 | 022Cr17Ni12Mo2 | SUS316L | 316L | S31603 | STS316L | 1.4404 | 02Cr17Ni12Mo2 | 316L | 316L |
| 15 | 0Cr17Ni12Mo2N | 06Cr17Ni12Mo2N | SUS316N | 316N | S31651 | STS316N | — | — | 316N | 316N |
| 16 | 00Cr17Ni13Mo2N | 022Cr17Ni13Mo2N | SUS316LN | 316LN | S31653 | STS316LN | 1.4429 | — | 316LN | 316LN |
| 17 | 0Cr18Ni12Mo2Cu2 | 06Cr18Ni12Mo2Cu2 | SUS316J1 | — | — | STS316J1 | — | — | 316J1 | 316J1 |
| 18 | 00Cr18Ni14Mo2Cu2 | 022Cr18Ni14Mo2Cu2 | SUS316J1L | — | — | STS316J1L | — | — | — | 316J1L |
| 19 | 0Cr19Ni13Mo3 | 06Cr19Ni13Mo3 | SUS317 | 317 | S31700 | STS317 | — | — | 317 | 317 |
| 20 | 00Cr19Ni13Mo3 | 022Cr19Ni13Mo3 | SUS317L | 317L | S31703 | STS317L | 1.4438 | — | 317L | 317L |
| 21 | 0Cr18Ni10Ti | 06Cr18Ni11Ti | SUS321 | 321 | S32100 | STS321 | 1.4541 | 04Cr18Ni10Ti20 | 321 | 321 |
| 22 | 0Cr18Ni11Nb | 06Cr18Ni11Nb | SUS347 | 347 | S34700 | STS347 | 1.4550 | 04Cr18Ni10Nb40 | 347 | 347 |
| Austenitic-Ferritic Stainless Steel (Duplex) | ||||||||||
| 23 | 0Cr26Ni5Mo2 | — | SUS329J1 | 329 | S32900 | STS329J1 | 1.4477 | — | 329J1 | 329J1 |
| 24 | 00Cr18Ni5Mo3Si2 | 022Cr19Ni5Mo3Si2N | SUS329J3L | — | S31803 | STS329J3L | 1.4462 | — | 329J3L | 329J3L |
| Ferritic Stainless Steel | ||||||||||
| 25 | 0Cr13Al | 06Cr13Al | SUS405 | 405 | S40500 | STS405 | 1.4002 | 04Cr13 | 405 | 405 |
| 26 | — | 022Cr11Ti | SUH409 | 409 | S40900 | STS409 | 1.4512 | — | 409L | 409L |
| 27 | 00Cr12 | 022Cr12 | SUS410L | — | — | STS410L | — | — | 410L | 410L |
| 28 | 1Cr17 | 10Cr17 | SUS430 | 430 | S43000 | STS430 | 1.4016 | 05Cr17 | 430 | 430 |
| 29 | 1Cr17Mo | 10Cr17Mo | SUS434 | 434 | S43400 | STS434 | 1.4113 | — | 434 | 434 |
| 30 | — | 022Cr18NbTi | — | — | S43940 | — | 1.4509 | — | 439 | 439 |
| 31 | 00Cr18Mo2 | 019Cr19Mo2NbTi | SUS444 | 444 | S44400 | STS444 | 1.4521 | — | 444 | 444 |
| Martensitic Stainless Steel | ||||||||||
| 32 | 1Cr12 | 12Cr12 | SUS403 | 403 | S40300 | STS403 | — | — | 403 | 403 |
| 33 | 1Cr13 | 12Cr13 | SUS410 | 410 | S41000 | STS410 | 1.4006 | 12Cr13 | 410 | 410 |
| 34 | 2Cr13 | 20Cr13 | SUS420J1 | 420 | S42000 | STS420J1 | 1.4021 | 20Cr13 | 420 | 420J1 |
| 35 | 3Cr13 | 30Cr13 | SUS420J2 | — | — | STS420J2 | 1.4028 | 30Cr13 | 420J2 | 420J2 |
| 36 | 7Cr17 | 68Cr17 | SUS440A | 440A | S44002 | STS440A | — | — | 440A | 440A |
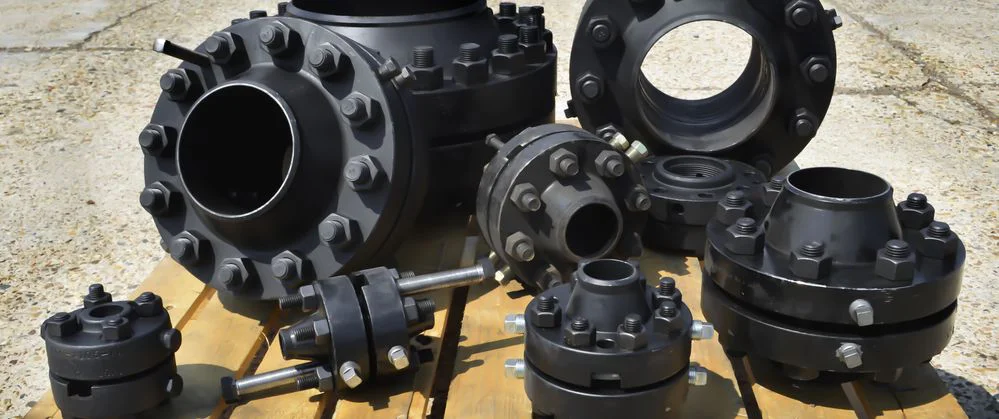

Special Flanges
Additionally, the flanges can be modified to form other types, depending on application and functions.
These unique designs are made to incorporate specific needs and applications, like reducing flanges to answer to size and orifice flanges to incorporate orifice mounting.

Incoloy 825 Flange
Industries Using
The basic application of the ASTM A182 SS 310/310S Flange to connect pumps, pipes, valves, and other equipment, often using butt welds, to make a pipework system.
Customized Alumina Ceramic Lined Project
Sort:99
High Chromium Alloy Lined Pipe
Sort:99
Sort:0
Wear-Resistant Hardfacing Liner Plate
Sort:0