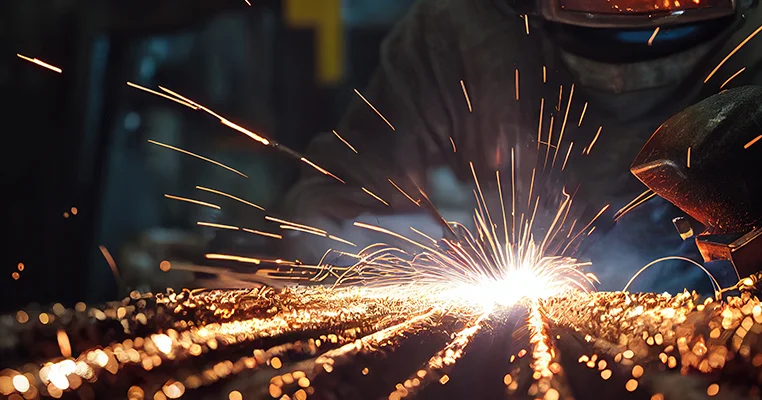

- How To Apply Wear-resistant Overlays
Hardfacing (hardface welding) deposits abrasion-resistant alloys onto base metals to extend component life in high-wear environments like mining, agriculture, and construction. proper preparation and technique selection are key to achieving strong, crack-free overlays.
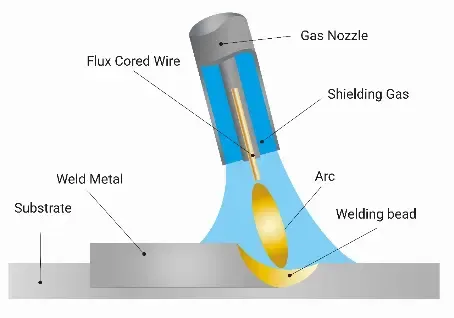
Hardfacing is a welding-based process used to deposit a harder, more wear-resistant alloy onto the surface of a base metal. This significantly improves resistance to abrasion, impact, and mechanical wear, thereby extending the service life of the component.
The process utilizes specialized electrodes or filler wires and is typically performed using conventional arc welding methods. During hardfacing, the filler material is melted and metallurgically bonded to the substrate, forming a durable protective layer.
The result is a dense, wear-resistant layer typically ranging from 1 to 10 mm in thickness. This hardfaced layer combines the properties of both the base metal and the deposited alloy, offering superior durability without replacing the entire component.
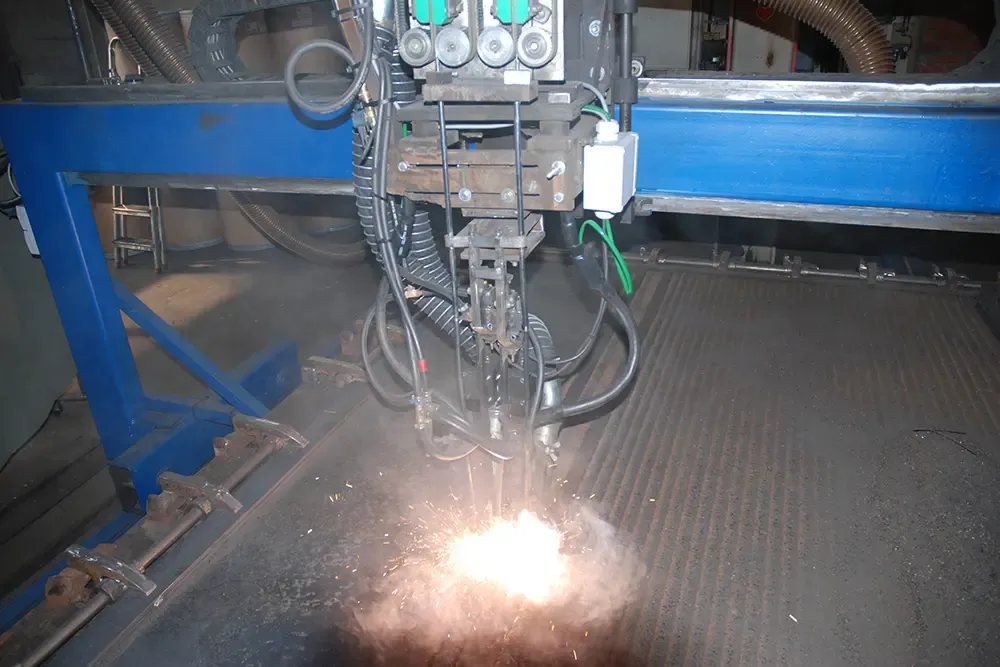
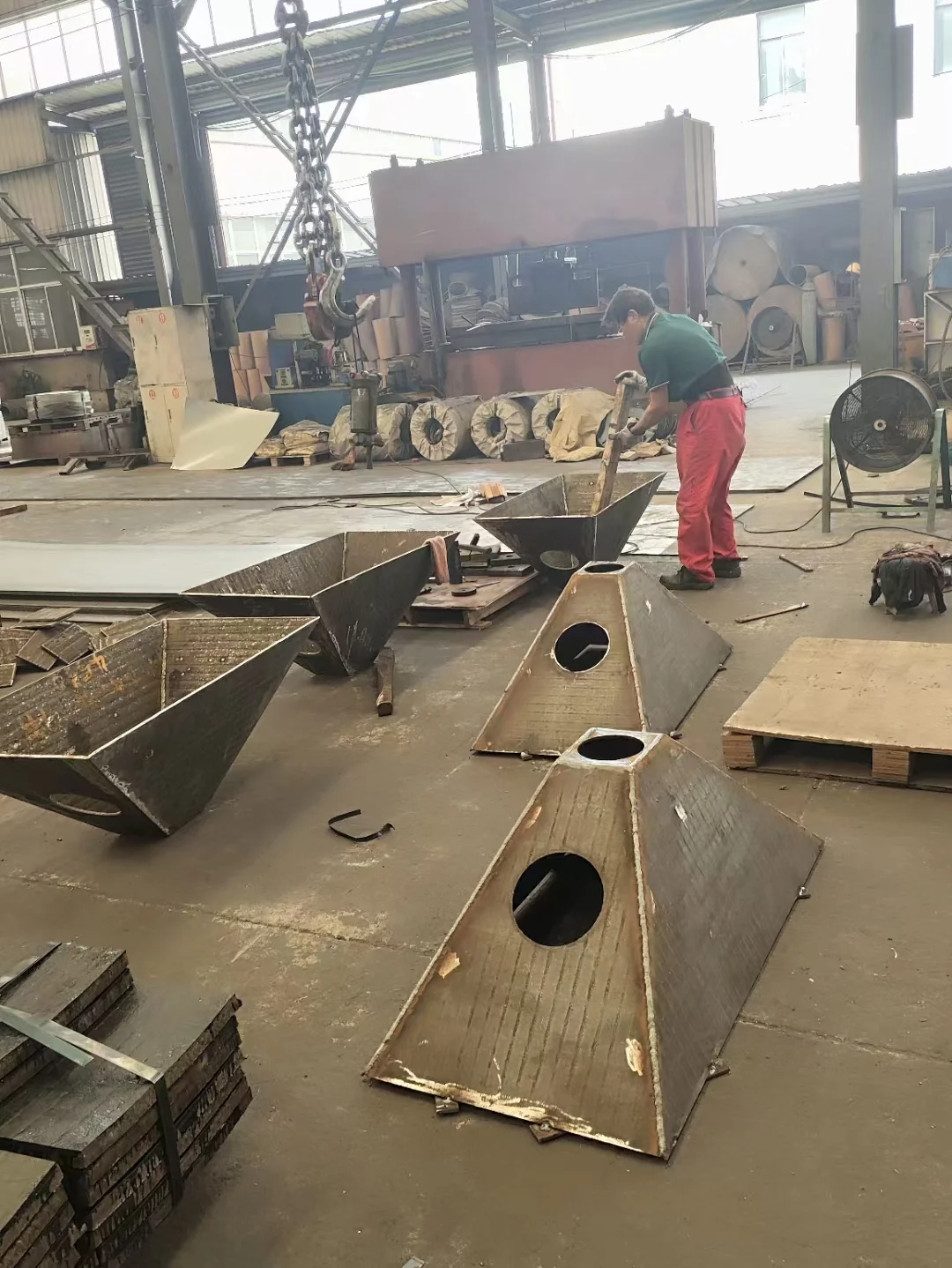
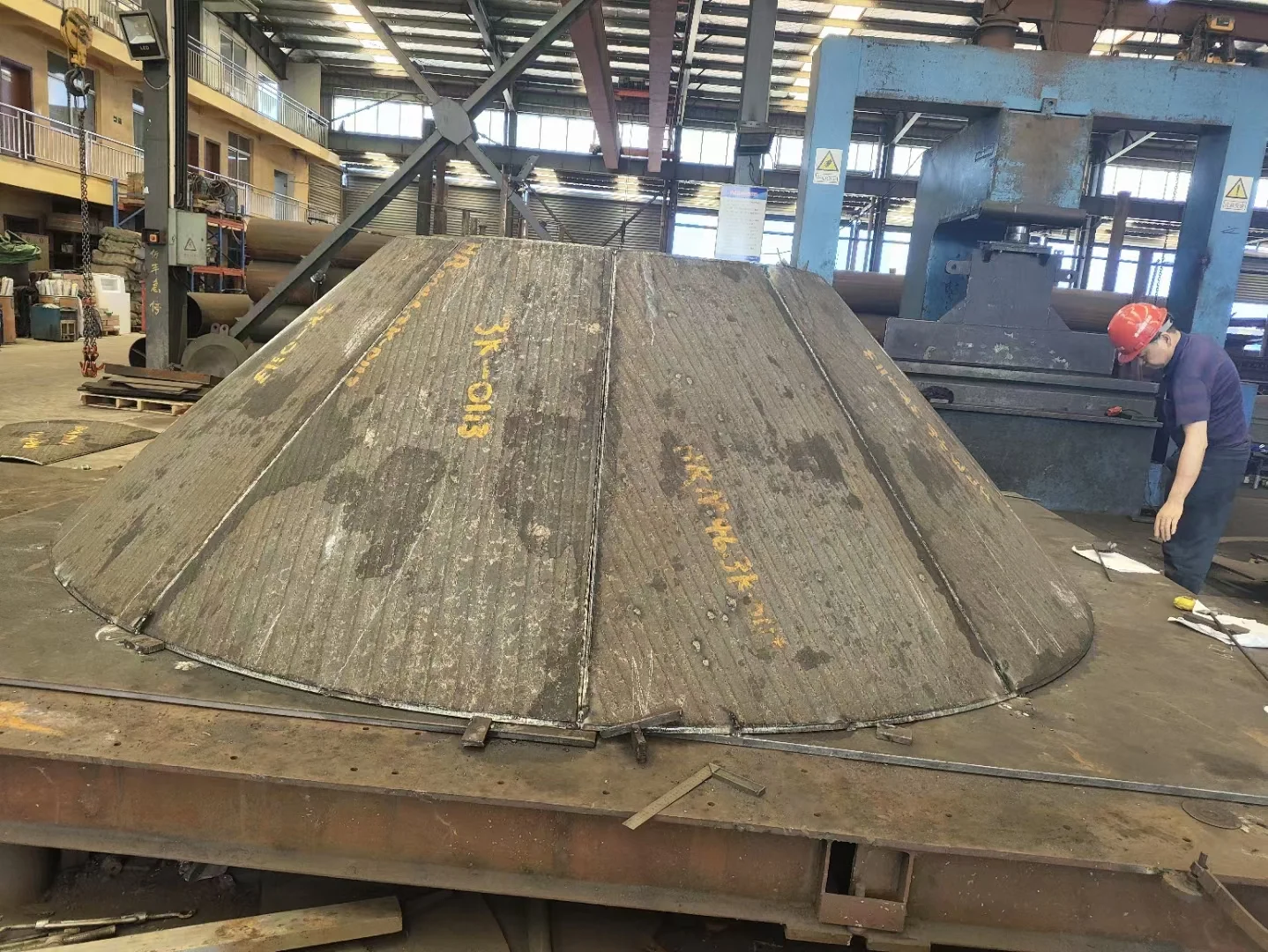
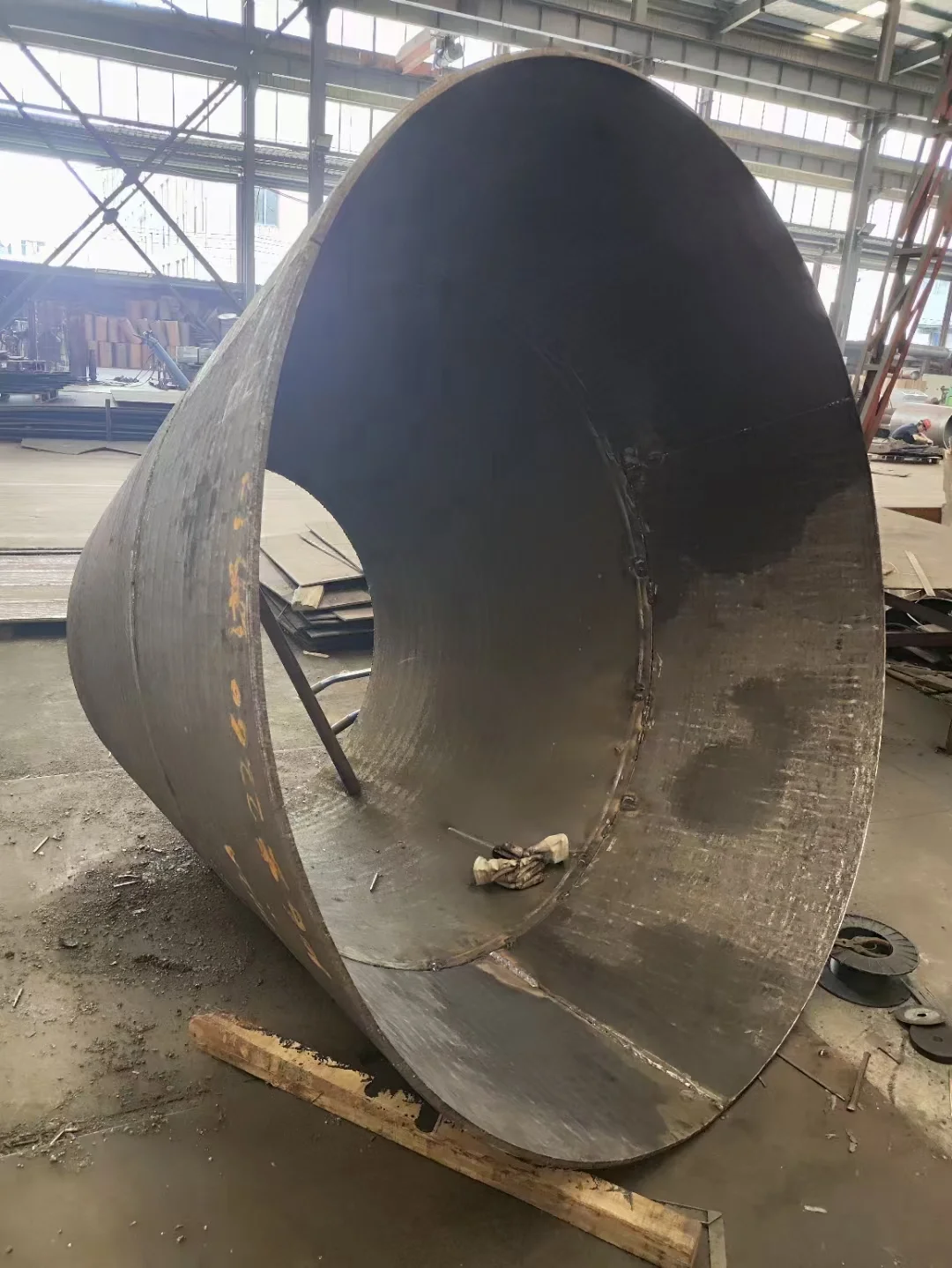
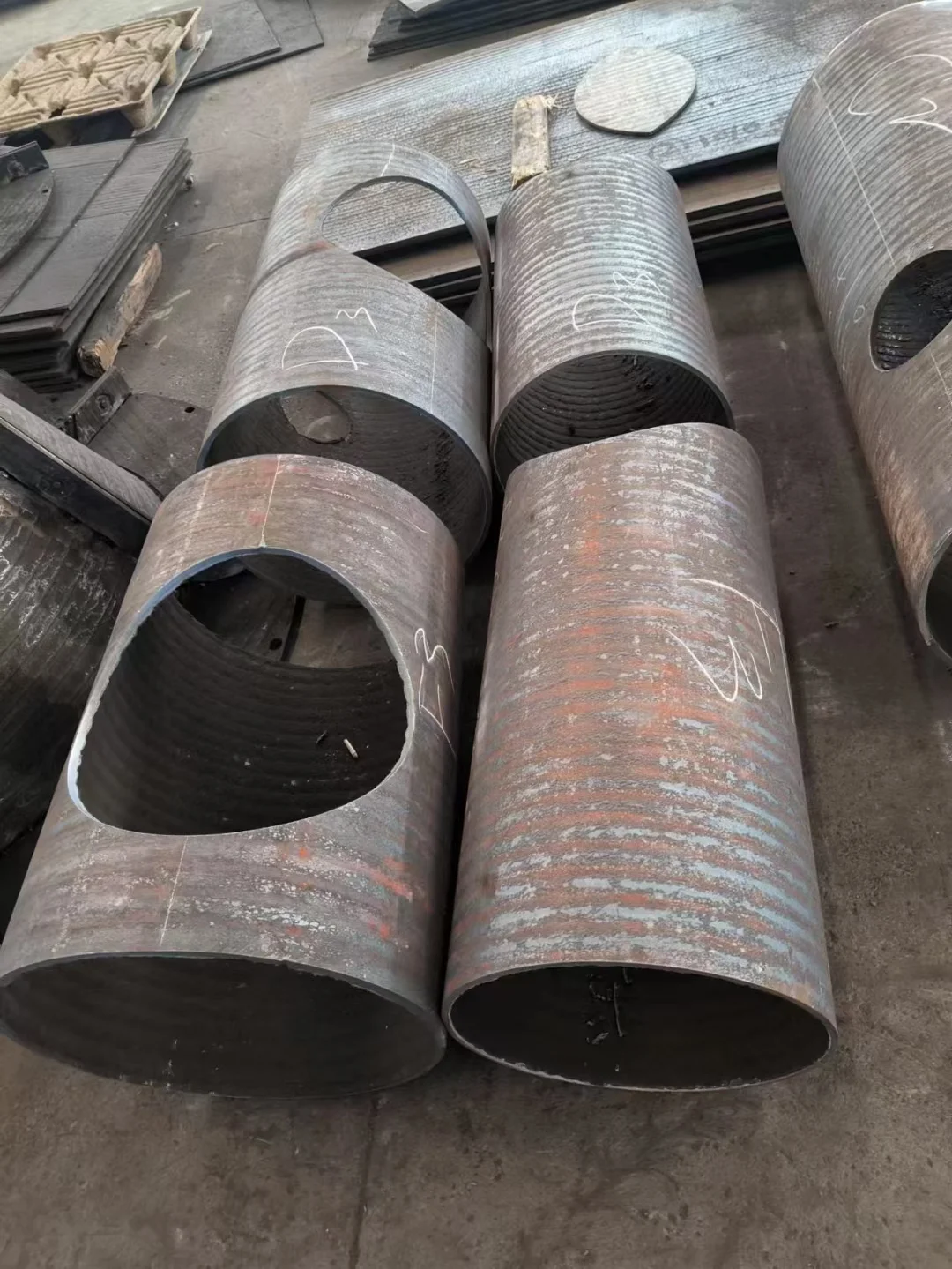
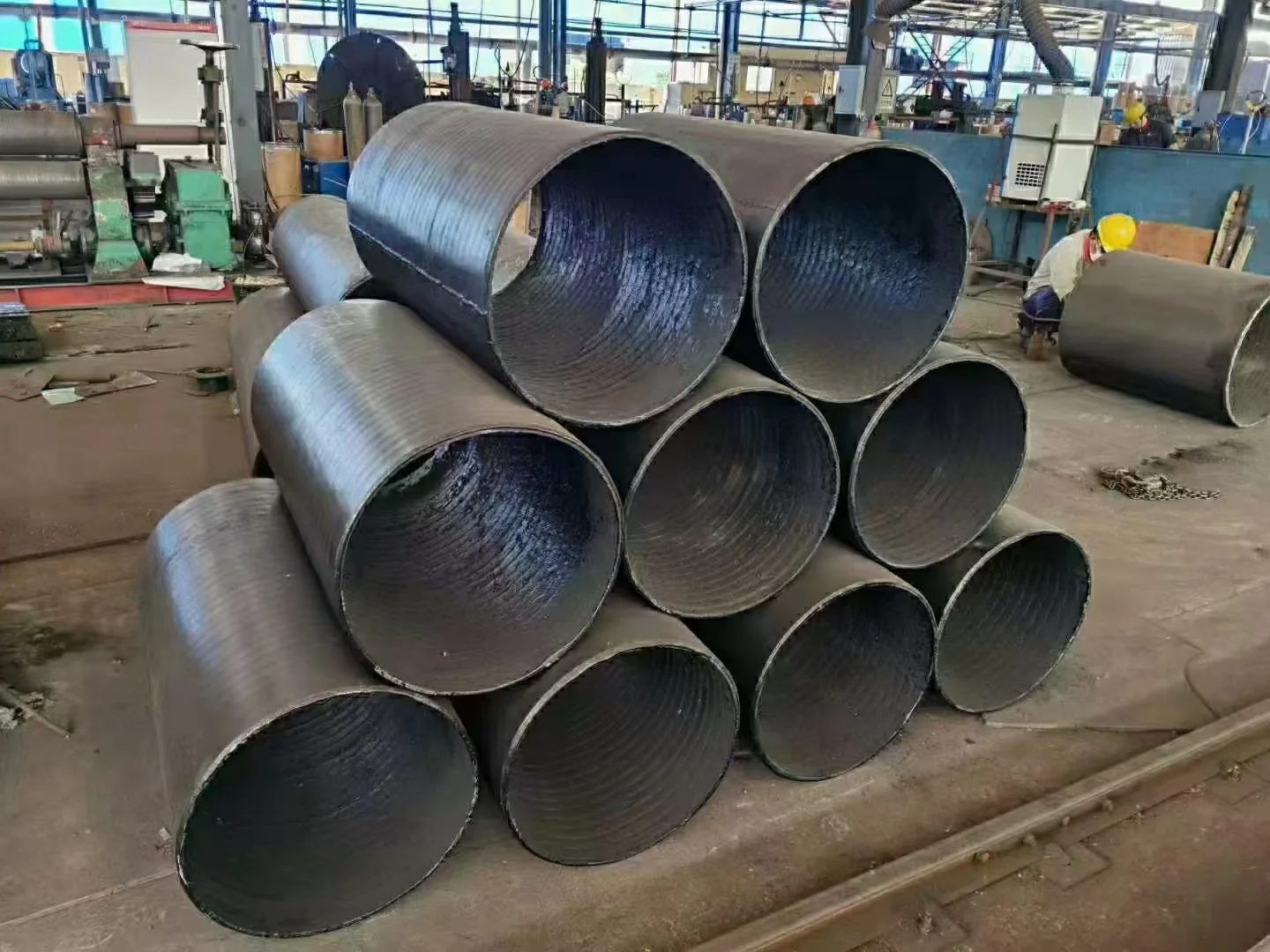
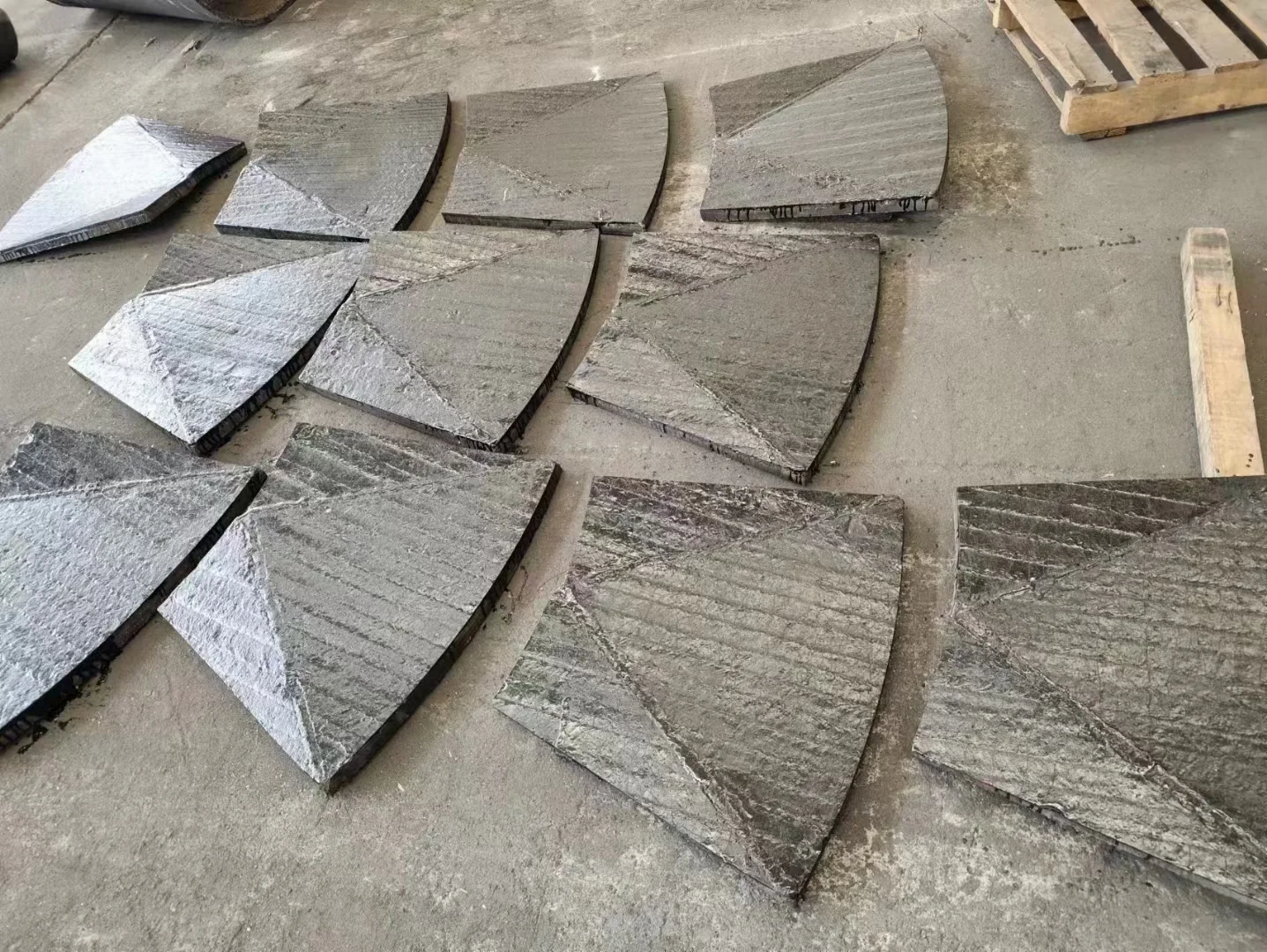
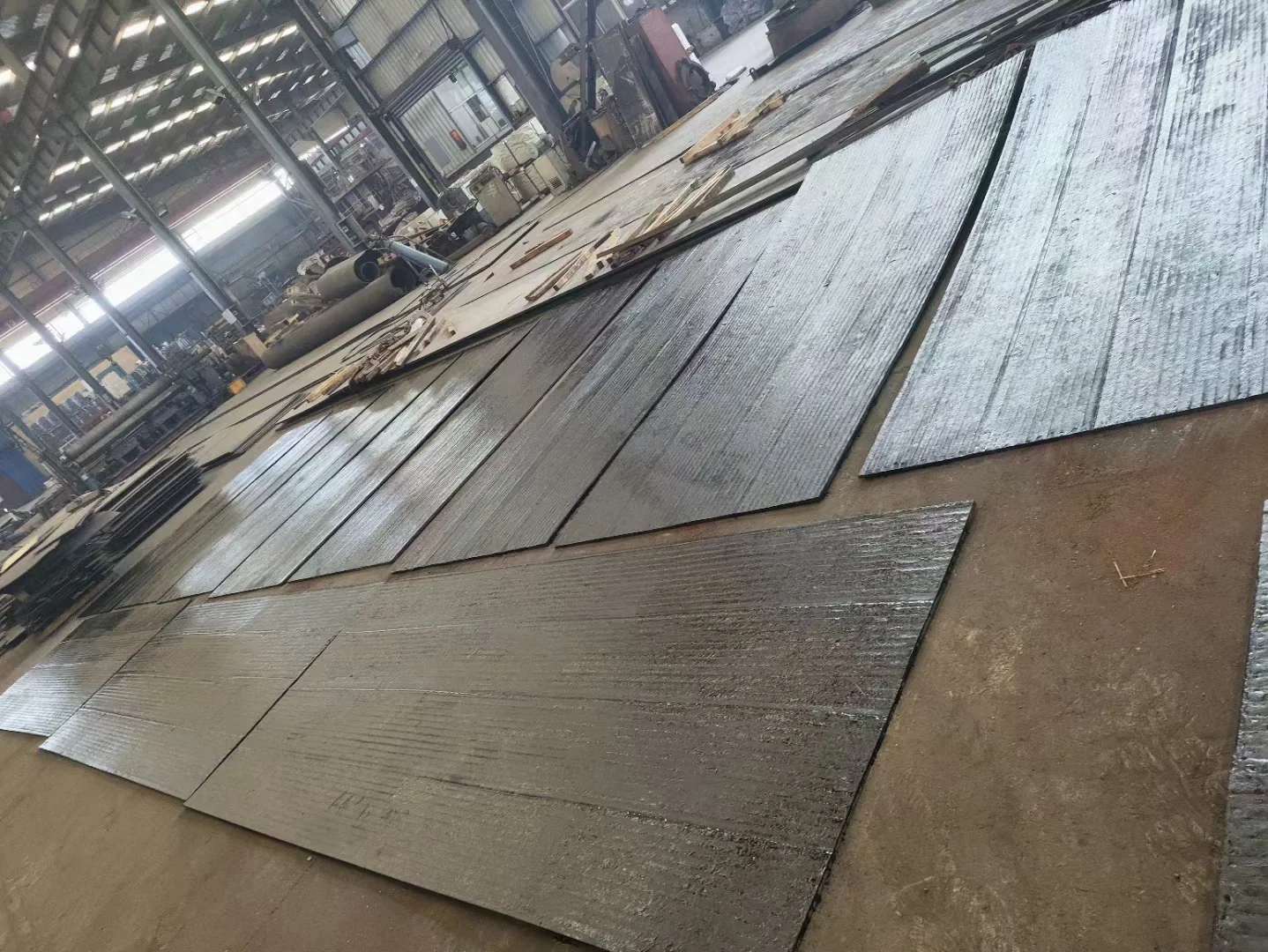










Hardfacing significantly improves resistance to abrasion and surface wear, extending the service life of metal components by up to 300%.
Ideal for mining, agriculture, and remote operations, hardfacing keeps equipment running while replacement parts are being manufactured or shipped.
By minimizing part replacement and reducing spare inventory, hardfacing can cut total replacement costs by 25%–75% over time.
Yes. Hardfacing is commonly performed using two primary techniques: Build-Up and Overlay. These methods are used either to restore worn components or to reinforce new or lightly used parts to extend their service life.
Used to repair heavily worn components with gouges, scratches, and surface loss by rebuilding the original working profile.
Additional weld material is carefully deposited in damaged areas, followed by leveling and finishing to restore functionality.
Applied to new or lightly worn parts using uniform weld passes to add a protective, wear-resistant layer.
Enhances durability and abrasion resistance without repair work, making it ideal for preventive reinforcement.
| Model | HRC | Working temperature | Alloy chemical composition | Specification and thickness Standard size 1400×3000 mm |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Cr | Mn | Nb | Others | ||||
| HP100 | 60-63 | >500℃ | 3-5 | 22-28 | 48 |
4+4, 5+5, 6+5, 6+6, 8+5, 8+6, 8+8, 10+5, 10+6, 10+7, 10+8, 10+10, 12+5, 12+6, 12+7, 12+8, 12+10, 12+12, 14+6, 14+8, 14+10, 16+4, 16+6, 16+8, 16+10, 16+12 |
||
| HP200 | 58-62 | >500℃ | 3-5 | 20-26 | 1-3 | 2-5 | ||
| HP300 | 60-65 | >800℃ | 4-6 | 18-25 | 2-3 | 5-8 | 3-6 | |
| HP400 | 50-55 | >500℃ | 0.4-2 | 3-7 | 15-20 | 2-5 | ||
Hardfacing
Hardfacing is a specialized welding process designed to extend the working life of metal parts by building a hard, wear-resistant surface over the base material. Unlike typical welds, hardfacing covers the entire working surface rather than just seams or cracks.
In reality, hardfacing is a special process that can be done with the only purpose of extending the service’s life of any equipment or surface. Now, if a metal part reaches a longer lifespan through hardfacing, more time can be used and fewer times will need to be replaced.
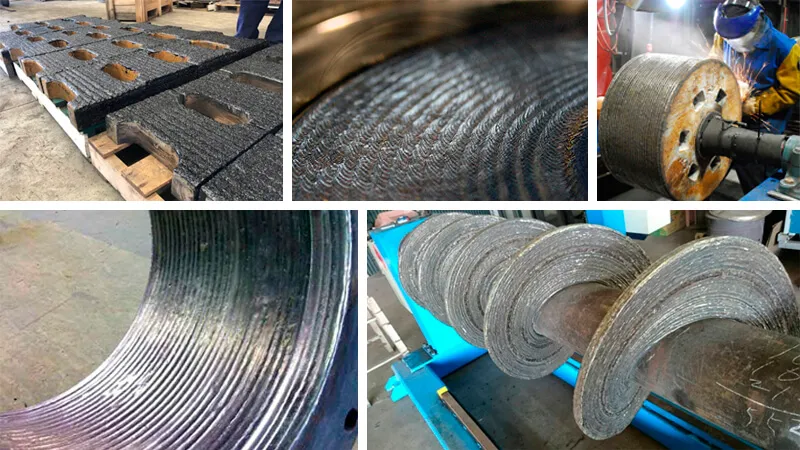

Hardfacing is the process to apply a tougher material to a base metal, to make it more durable or extend its lifespan. This harder material is welded to the base metal by using specialized electrodes or filler rods.
They are meant to form very dense and thick layers (between 1 to 10 mm) above the base metal of wear-resistant material with high bond strength. The coating material can add ductility, hardness, corrosion resistance, and erosion resistance to the original part.
Other names given to hardfacing are hard surfacing, surface welding, and cladding. Among the base metals that can be hardfaced are the following ones:
Before starting any hardfacing process is needed to identify exactly what material is made the part of because this defines the pre-heat and post-heat temperature that should be applied.
All metal parts even with normal use will wear as time goes by. This may cause them to lose their functionality and as a result, the need for a new part.
In certain industrial applications, like in mining or agriculture, this may happen more frequently. Hardfacing can be an ideal option for any metal part that may wear for being used. In short, hardfacing can help to:
Industrial equipment is intended to last for many years. So, many companies take some years to replace theirs.
Take away any rust, grime, oil, grease, or gunk that the workpiece may have. If there is any previous hardfacing layer, take it out to avoid any cracking.
The part may have an indent caused by an impact. In that case, fill the space before applying layers. Some people know this step as rebuilding because the purpose is to restore the piece to its original dimensions.
This step is also known as a buffer layer. The objective is to overcome the possible incompatibility between the metal base and the final coating. By doing this, shrinkage cracks from the hardfacing to the base metal can be avoided.
Here is when the job is done. This consists of the addition of coating layers to the workpiece. Normally 3 layers are the most you can add but are unlimited when using certain materials.
In short, hardfacing is the option for any company trying to save in parts or equipment with a high rate of abrasion or erosion. Some of the many industries in which hardfacing is quite popular or convenient are:
But this list does not pretend to be exclusive, so despite your industry not being there, chances are hardfacing may be an option for you.

HARD FACING
Hardfacing is widely used in applications where components are exposed to continuous impact, abrasion, or erosion. By reinforcing the working surface, it helps equipment maintain strength, dimensions, and performance over extended service periods.

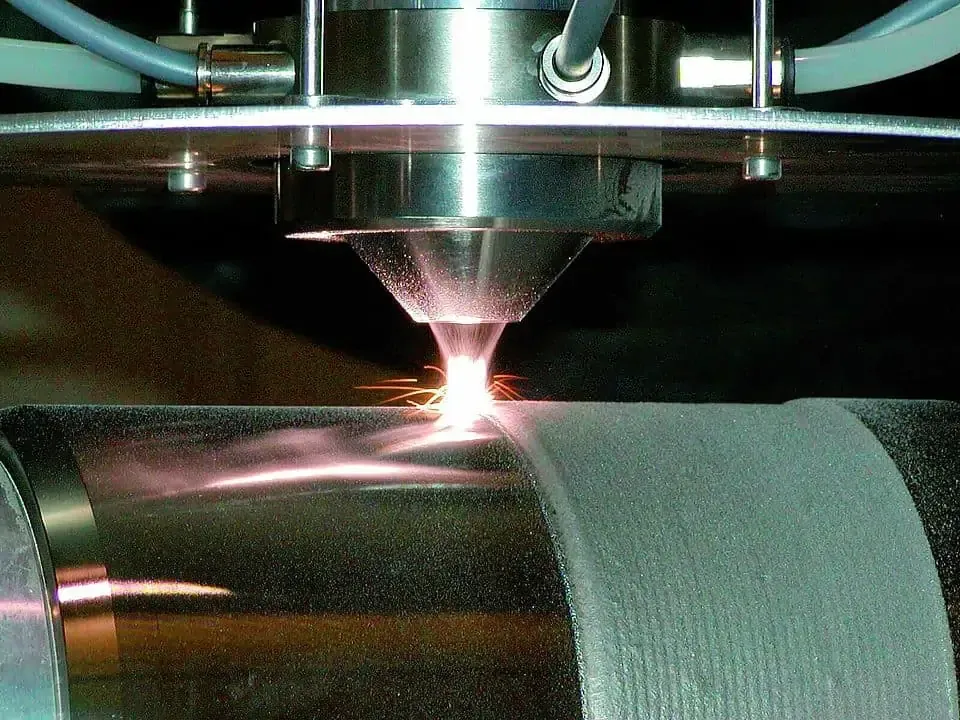
Common welding techniques used in hardfacing applications:
Sort:109
Rare Earth Alloy Wear Resistant Pipe
Sort:103
Sort:0