ASTM A335 P5
Alloy seamless pipes

15CrMoG is a high-alloy steel grade widely used in the manufacturing of boiler tubes and pressure vessels, particularly for applications that require high strength and resistance to oxidation and corrosion at elevated temperatures.
15CrMoG steel tubes are also used in:
15CrMoG is GB 5310-95 steel grade (equivalent to 13CrMo44 of Federal Germany; corresponding to 1Cr-1 / 2Mo and 1 1 / 4cr-1 / 2mo-si steel widely used in various countries in the world). Its chromium content is higher than 12CrMo steel, so it has higher thermal strength at 500-550 ℃. When the temperature is higher than 550 ℃, the thermal strength of 15CrMoG steel is significantly reduced. When it runs at 500-550ec for a long time, it does not produce graphitization, but it will produce carbide spheroidization and redistribution of alloy elements, which all lead to the decrease of the thermal strength of steel. 15CrMoG steel has good relaxation resistance at 450 ℃. Its pipe making and welding process performance is good.
15CrMoG alloy pipe is a seamless steel tube, its performance is much higher than the general seamless steel pipe, because the inside of this tube contains CR more, its alloy steel tube high temperature, low-temperature, corrosion resistance of other seamless steel tubes, so the alloy tube in the petroleum, chemical, electric power, boiler and other industries are more widely used.
The range of 15CrMoG alloy pipe sizes that may be examined by each method shall be subjected to the limitations in the scope of the respective practice.
For high-pressure boiler (working pressure 9.8MPa or more generally, the working temperature between 450℃-650℃) of heating surface tubes, header, economizer, superheater, reheater and so on.
The range of 12Cr1MoVG pipe sizes that may be examined by each method shall be subjected to the limitations in the scope of the respective practice.
15CrMoG alloy pipe is widely used in industries such as power generation, petrochemical, and boiler manufacturing, where it is used for superheaters, reheaters, steam pipes, and other components that operate at elevated temperatures and pressures. Its excellent mechanical properties, high-temperature strength, and resistance to creep make it suitable for demanding environments where resistance to corrosion, oxidation, and high-temperature stress is required.
15CrMoG alloy pipe is a type of high-temperature and high-pressure steel pipe known for its exceptional strength, toughness, and resistance to corrosion and oxidation. It belongs to the family of alloy steels, which are specially designed to withstand challenging environments and demanding industrial applications. The "15CrMoG" designation refers to its chemical composition, with 15% chromium and molybdenum being the main alloying elements.
Standard: GB 5310
Relative grades: 20G, 20MnG, 15MoG, 15CrMoG, 12Cr2MoG, 12Cr1MoVG. After consultation, can also supply other grades of steel.
15CrMoG Alloy steel pipe is a seamless steel tube, its performance is much higher than the general seamless steel pipe, because the inside of this tube contains CR more, its alloy steel tube high temperature, low-temperature, corrosion resistance of other seamless steel tubes, so the alloy tube in the petroleum, chemical, electric power, boiler and other industries are more widely used.
The chemical composition of 15CrMoG alloy pipe plays a crucial role in its mechanical properties and performance. The presence of 15% chromium and molybdenum imparts excellent high-temperature strength and creep resistance. Additionally, the alloy contains carbon, manganese, silicon, and small amounts of other elements, contributing to its overall properties.
The chemical composition of 15CrMoG alloy steel is as follows:
| Material | C | Mn | Si | Cr | Mo | Ni | Nb+Ta | S | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15CrMo | 0.12~0.18 | 0.40~0.70 | 0.17~0.37 | 0.80~1.10 | 0.40~0.55 | ≤0.30 | _ | ≤0.035 | ≤0.035 |
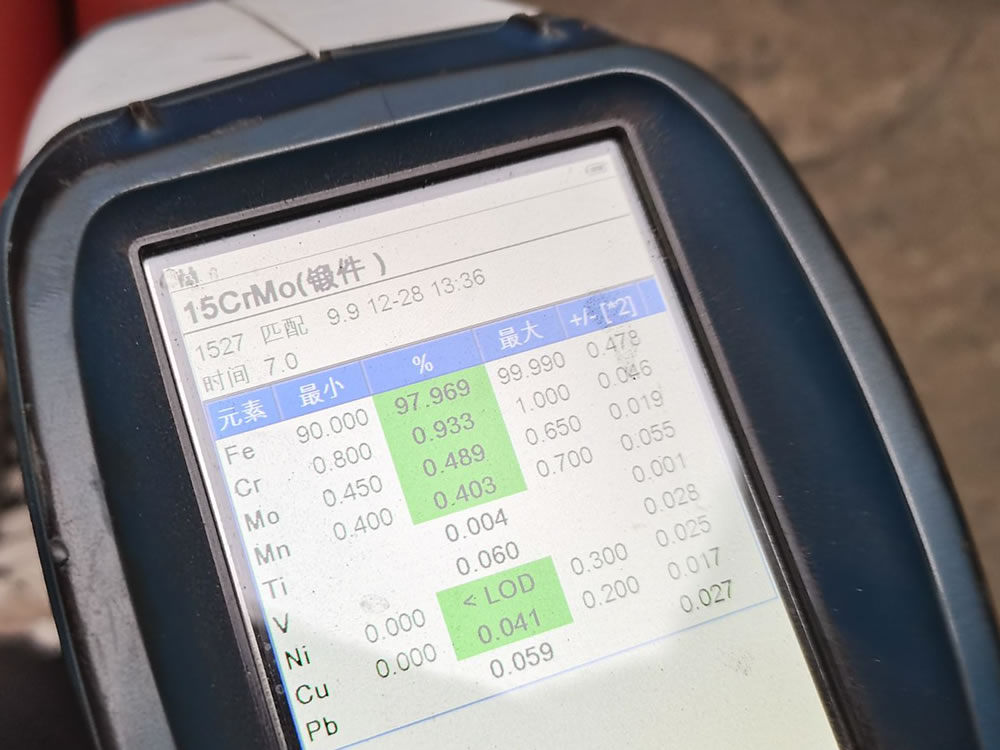
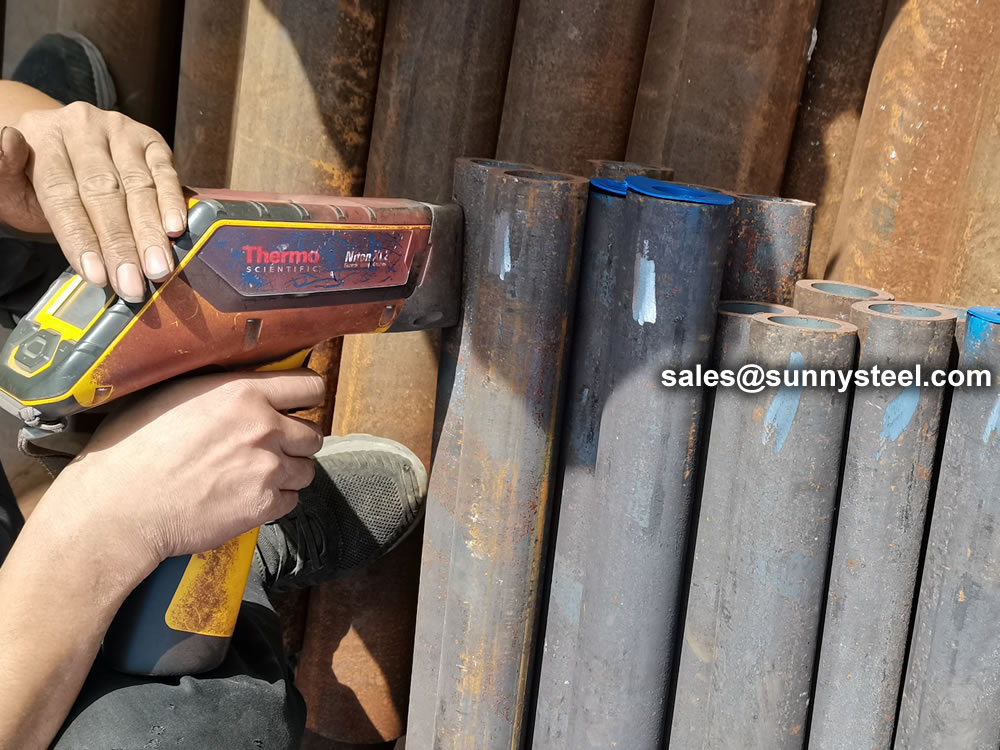
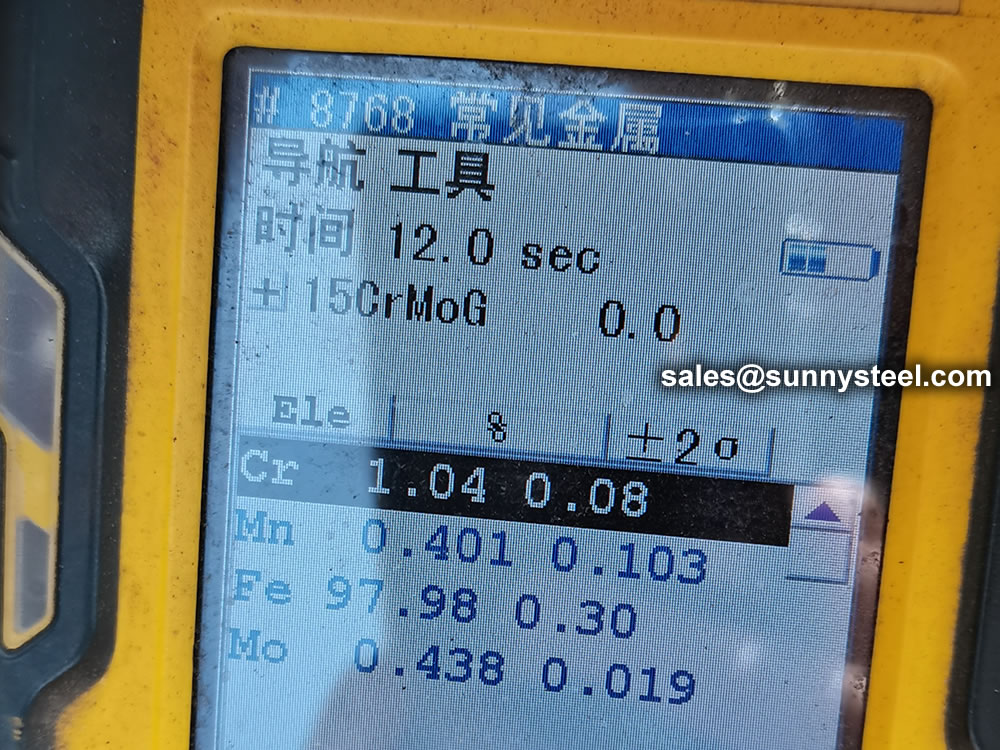
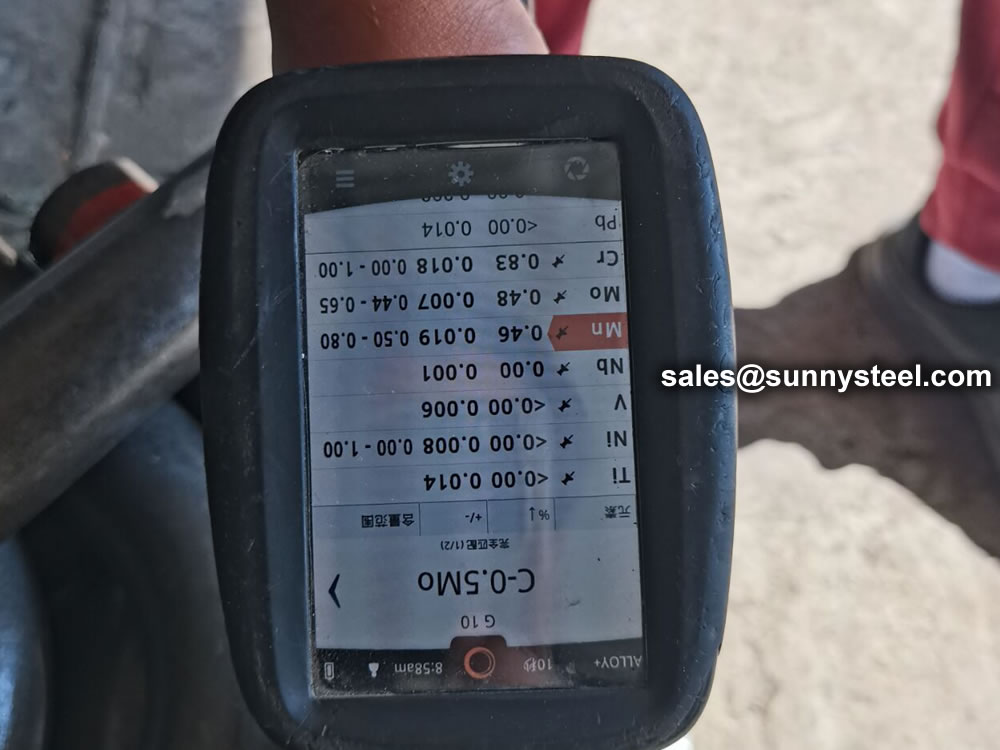
To perform a PMI test on a 15CrMoG alloy pipe, you typically use handheld or portable X-ray fluorescence (XRF) analyzers or optical emission spectrometers.







| Material | Yield strength σs/MPa (>=) | Tensile strength σb/MPa (>=) | Elongation δ5/% (>=) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15CrMo | 440~640 | 235 | 21 |
The mechanical properties of 15CrMoG alloy pipe are impressive, making it suitable for use in extreme conditions. It exhibits high tensile strength, superior toughness, and exceptional resistance to deformation under high pressures and temperatures.
| Country | Standard | Material |
|---|---|---|
| USA | SAE/AISI/UNS | - |
| Germany | DIN,WNr | 15CrMO | 1.7262 |
| China | GB | 15CrMo |
| Japan | JIS | SCM415 |
| France | AFNOR | 15CD4.05 |
| England | BS | 1501-620 | Cr31 |
| Italy | UNI | - |
| Poland | PN | - |
| Czechia | CSN | - |
| Austria | ONORM | - |
| Sweden | SS | - |
| Spain | UNE | - |
Heat treatment is a highly effective means of improving and modifying the properties of 15CrMo alloy round steel. It plays a very important role in product reliability and economy. Heat treatment of 15CrMo alloy round steel usually includes ordinary heat treatment (annealing, normalising, quenching, tempering) and surface heat treatment (surface quenching and chemical heat treatment - carburising, nitriding, metallising, etc.).
In mechanical engineering, many machine parts, such as crankshafts, gears, camshafts of internal combustion engines and gears in important reduction gears, require not only sufficient toughness, plasticity and bending strength in the core, but also a high surface thickness within a certain thickness. hardness, high wear resistance and high fatigue strength. It is difficult to meet the above performance requirements simultaneously with the above various overall heat treatment methods, and the use of surface heat treatment is the most effective method to meet these performance requirements simultaneously.
Surface heat treatment is a heat treatment method that changes the surface properties of 15CrMo alloy round steel by changing the structure of the surface layer.
Surface quenching is a heat treatment that gradually changes the surface structure without changing the chemical composition of the surface. It can be carried out by high-frequency, medium-frequency or power-frequency induction heating method or flame heating method. The common feature is that the surface of 15CrMo alloy round steel is quickly heated to the quenching temperature, and when the heat is not transferred to the core of the part, it is quickly cooled, so that the surface hardness is high, but the core still has high toughness.
Chemical heat treatment is a heat treatment method that changes the chemical composition and structure of the surface layer of 15CrMo alloy round steel. Chemical heat treatment can be divided into methods such as carburizing, nitriding, carbonitriding and metallising according to the different elements infiltrated on the surface of 15CrMo alloy round steel. It is very effective in improving and enhancing the wear resistance, corrosion resistance and fatigue resistance of 15CrMo alloy round steel. At present, chemical heat treatment has developed rapidly, and there are many applications of new technologies.
15CrMoG alloy pipe heat treatment: Normalizing and tempering
| W.T.(S) | Tolerance of W.T. | |
|---|---|---|
| <3.5 | +15%(+0.48mm min) | |
| -10%(+0.32mm min) | ||
| 3.5-20 | +15%,-10% | |
| >20 | D<219 | ±10% |
| D≥219 | +12.5%,-10% | |
The principle of purifying hydrogen from 15CrMoG alloy pipe is that, at 300-500 ℃, hydrogen is adsorbed on the side of the 15CrMoG alloy steel tube, and the hydrogen is absorbed on the 1515CrMoG alloy steel pipe wall, because of the lack of two electrons in the 4d electron layer of palladium, It can produce unstable chemical bonds with hydrogen (this reaction of palladium and hydrogen is reversible), under the action of Palladium, hydrogen is ionized to proton its radius is 1.5x1015m, and the lattice constant of palladium is 3.88x10-10m (20 ℃), so it can pass 15CrMoG alloy steel pipe, Under the action of Palladium, protons are combined with electrons to form hydrogen molecules, escaping from the other side of the 15CrMoG alloy steel tube.
For high-pressure boiler (working pressure 9.8MPa or more generally, the working temperature between 450℃-650℃) of heating surface tubes, header, economizer, superheater, reheater and so on.
Classification, code
a) Hot rolled steel pipe, codenamed WH;
b) Cold drawn steel pipe, codenamed WC.
The steel tubes shall be delivered in a heat treated condition.
Length: 5800mm; 6000mm; 6096mm; 7315mm; 11800mm; 12000mm; and so on.
Max length: 16000mm, also U bending can be offered.
This inventory is part of the inventory, demand and other models in stock or order materials, please contact us.


15CrMoG high pressure alloy pipe is a steel widely used in the electric power industry.
It has high thermal strength when used at 500℃-550℃. When the operating temperature is higher than 550℃, its thermal strength performance is significantly reduced. Usually, 15CrMo steel is mainly used for high and medium pressure tubes and steam tubes with steam parameters of 510°C, and heat exchanger tubes with tube wall temperature of 550°C.
With years of expertise, we provide a diverse array of steel tube processing options. From sawing and machining tube blanks to intricate bending and upsetting operations, we actively assist you throughout your projects.
Our capabilities extend to eccentricity reduction and concentricity enhancement through turning and grinding. We excel in creating complex geometries using processes like rotary swaging and axial forming. Additionally, we offer property modifications via partial heat treatment, ensuring tailored solutions for your specific needs.












Seamless steel pipe is regularly used in the transportation of fluids such as water, natural gas, waste and air. It is also regularly required in many high-pressure, high-corrosive environments such as in the oil & gas, power generation and pharmaceutical industries. Some common uses of seamless pipes include:
Chemical composition inspection, mechanical properties test(tensile strength,yield strength, elongation, flaring, flattening, bending, hardness, impact test), surface and dimension test,no-destructive test, hydrostatic test.
identification of the chemical composition of the metal used to manufacture the fitting. Uses PMI sensors, including X-ray fluorescence or optical emission spectrometry.




















Steel pipe delivery status(condition): cold / hard (BK), cold / soft (BKW), after cold stress relief annealing (BKS), annealing (GBK), normalized (NBK).
| Term | Symbol | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Cold-finished/hard (cold-finished as-drawn) | BK | No heat treatment after the last cold-forming process. The tubes therefore have only low deformability. |
| Cold-finished/soft (lightly cold-worked) | BKW | After the last heat treatment there is a light finishing pass (cold drawing) With proper subsequent processing, the tube can be cold-formed (e.g. bent, expanded) within certain limits. |
| Annealed | GBK | After the final cold-forming process the tubes are annealed in a controlled atmosphere or under vacuum. |
| Normalized | NBK | The tubes are annealed above the upper transformation point in a controlled atmosphere or under vacuum. |

The general cold strip mills, volume should go through continuous annealing (CAPL unit) to eliminate cold hardening and rolling stress, or batch annealing reach the mechanical properties of the corresponding standard specifies. Cold rolled steel surface quality, appearance, dimensional accuracy better than hot-rolled plate, and right-rolled thin product thickness is about 0.18mm, so the majority of users favor.
Cold rolled steel coil substrate products deep processing of high value-added products. Such as electro-galvanized, hot dip galvanized, electro-galvanized fingerprint resistant, painted steel roll damping composite steel, PVC laminating steel plates, etc., so that the excellent quality of these products has a beautiful, high resistance to corrosion, has been widely used.
Cold rolled steel coil finishing after annealing, cut the head, tail, trimming, flattening, smooth, heavy volume, or longitudinal clipboard. Cold-rolled products are widely used in automobile manufacturing, household electrical appliances, instruments, switches, buildings, office furniture and other industries. Steel plate strapping package weight of 3 to 5 tons. Flat sub-volume typically 3 to 10 tons / volume. Coil diameter 6m.
Bare packing/bundle packing/crate packing/wooden protection at the both sides of tubes and suitably protected for sea-worthly delivery or as requested.












There are probably hundreds of different methods for packing a pipe, and most of them have merit, but there are two principles that are vital for any method to work prevent rusting and Sea transportation security.
Our packing can meet any needs of the customers.
Our team of experienced sales specialists proudly partners with gas and chemical processors, power generation plants, oil refineries, and related industries to offer piping components and value-added services.
Alloy steels are made by combining carbon steel with one or several alloying elements, such as manganese, silicon, nickel, titanium, copper, chromium and aluminum. These metals are added to produce specific properties that are not found in regular carbon steel. The elements are added in varying proportions (or combinations) making the material take on different aspects such as increased hardness, increased corrosion resistance, increased strength, improved formability (ductility); the weldability can also change.
Commonly used alloying elements and their effects are listed in the table given below.
| Alloying Elements | Effect on the Properties |
|---|---|
| Chromium | Increases Resistance to corrosion and oxidation. Increases hardenability and wear resistance. Increases high temperature strength. |
| Nickel | Increases hardenability. Improves toughness. Increases impact strength at low temperatures. |
| Molybdenum | Increases hardenability, high temperature hardness, and wear resistance. Enhances the effects of other alloying elements. Eliminate temper brittleness in steels. Increases high temperature strength. |
| Manganese | Increases hardenability. Combines with sulfur to reduce its adverse effects. |
| Vanadium | Increases hardenability, high temperature hardness, and wear resistance. Improves fatigue resistance. |
| Titanium | Strongest carbide former. Added to stainless steel to prevent precipitation of chromium carbide. |
| Silicon | Removes oxygen in steel making. Improves toughness. Increases hardness ability |
| Boron | Increases hardenability. Produces fine grain size. |
| Aluminum | Forms nitride in nitriding steels. Produces fine grain size in casting. Removes oxygen in steel melting. |
| Cobalt | Increases heat and wear resistance. |
| Tungsten | Increases hardness at elevated temperatures. Refines grain size. |

When you partner with Sunny Steel, you can stop worrying about meeting deadlines thanks to our responsive and timely service. You'll also say goodbye to unnecessary shopping around. Instead, you'll get white glove service from an expert who understands your needs and can get you the materials you need quickly.
