
17-4PH is a precipitation hardened(PH) martensitic stainless steel consisted of copper and niobium/tantalum.
17-4 PH Stainless Steel is a precipitation hardening martensitic stainless steel. It is typically used in applications where high strength and a moderate level of corrosion resistance are required. The desired strength and toughness can be manipulated by the tempering range in the heat treatment process.
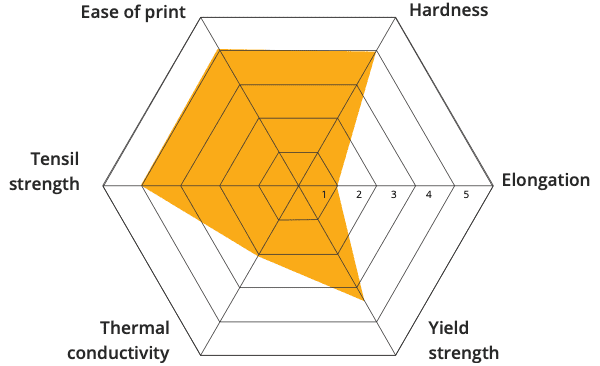
17-4PH mechanical properties can be optimized by heat treatment with the compression strength achieving up to 1100-1300 mpa (160-190 ksi). This type can be strengthened by directly obtaining martensite structure after solution treatment. With subsequent aging treatment, the precipitation hardened phase (including copper phase) is further strengthened. Due to low carbon content, it features better workability, corrosion resistance and weldability than Martensitic Stainless Steels such as Cr13 and 9Cr18 and 1Cr17Ni2.
17-4 stainless steel is a popular alloy, and for good reason: it offers excellent corrosion resistance, strength, and versatility. Whatever the application you need it for, our team can help ensure you have the right material for the job.
Ideal for high
temperature applications
Superior formability
and weldability
Excellent
corrosion resistance,
toughness and strength
17-4 stainless steel is a type of alloy that contains about 17% chromium and 4% nickel. This combination makes it ideal for use in high temperature applications – including within the gas, chemical, and aviation industries – because the alloy exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, mechanical properties, toughness, and strength even in temperatures up to 600 degrees Fahrenheit (316°C). It also has superior formability and weldability compared to other grades of stainless steel.
17-4 stainless steel, otherwise known as SAE Type 630, is frequently used with operations demanding high tensile strength and a middling level of corrosion resistance. 17-4 PH is the most-used grade of martensitic precipitation hardenable alloys and is regarded as the most broadly formed precipitation hardening grade. Its intense tensile strength keeps its ductility and hardness at high temperatures while still demonstrating exceptional corrosion resistance in all conditions.
17-4 PH Stainless Steel is a precipitation hardening martensitic stainless steel. Typical usage is seen in applications requiring high strength and a modest level of corrosion resistance. Strength and toughness desired can be manipulated by temperate range in the heat treatment process.
17-4PH stainless steel is a grade of martensitic precipitation hardened stainless steel can be heat treated to high levels of strength and hardness, features corrosion resistance and machinability comparable to austenitic 304 stainless.
This versatile material is widely used in aerospace, chemical, petrochemical, food processing, paper and general metalworking industries.

| Element | Content |
|---|---|
| Carbon | 0.07% (Max) |
| Silicon | 1.00% (Max) |
| Manganese | 1.00% (Max) |
| Phosphorous | 0.040% (Max) |
| Sulfur | 0.030% (Max) |
| Chromium | 15% - 17.5% |
| Molybdenum | 0.50% (Max) |
| Nickel | 3% - 5% |
| Copper | 3% - 5% |
*Not exclusively to the element mentioned, but that one predominates other elements that are used in smaller quantities.
| Material | Condition | Ultimate Tensile Strength (ksi) |
0.2 % Yield Strength (ksi) |
Elongation % in 2D | % Reduction of Area | Rockwell C Hardness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alloy 17-4 PH Bar AMS 5643 |
Cond A | – | – | – | – | 363 HB max |
| Alloy 17-4 PH Bar AMS 5643 |
H900 | 190 | 170 | 10 | 40 | 388-444 |
| Alloy 17-4 PH Bar AMS 5643 |
H925 | 170 | 155 | 10 | 44 | 375-429 |
| Alloy 17-4 PH Bar AMS 5643 |
H1025 | 155 | 145 | 12 | 45 | 331-401 |
| Alloy 17-4 PH Bar AMS 5643 |
H1075 | 145 | 125 | 13 | 44 | 311-375 |
| Alloy 17-4 PH Bar AMS 5643 |
H1100 | 140 | 115 | 14 | 45 | 302-363 |
| Alloy 17-4 PH Bar AMS 5643 |
H1150 | 135 | 105 | 16 | 50 | 277-352 |
Stainless Steel 17-4PH reacts best to hot forming at 1742 to 2192 °F (950 to 1200 °C), with annealing at 76 °F (25 °C) and aging. The alloy can also be cold-formed in limited form, primarily to plates in the annealed condition. However, stress corrosion resistance can be improved with re-aging.
Furthermore, 17-4PH can be cut using mechanical operations, such as abrasive waterjets, machining, bandsaw, and shearing. However, plasma cutting isn’t recommended on this alloy.
17-4PH has the best welding characteristics of competing stainless steel alloys. Moreover, it can be welded using all standard techniques, including gas tungsten arc, gas metal arc, shielded metal arc, and plasma arc. To achieve desired mechanical properties, pre-weld and post-weld heat treatments are recommended. For the best results, we recommend the AMS 5643 wire.
17-4 PH is also known as stainless steel grade 630. The advantage of precipitation hardening steels is that they can be supplied in a “solution treated” condition, which is readily machinable.
Alloy 17-4 PH withstands corrosive attacks better than any of the standard hardenable stainless steels and is comparable to Alloy 304 in most media. If there are potential risks of stress corrosion cracking, the higher aging temperatures then must be selected over 1022°F (550°C), preferably 1094°F (590°C).
General applications for 17-4 PH include aircraft and gas turbines, chemical processing equipment, oil and petroleum refining equipment, and food processing equipment. Type 17-7 PH stainless steel is a Chromium-Nickel-Aluminum, semi-austenitic stainless steel.
High-alloy steels like 17-4PH Stainless Steel offer many advantages over other metals for a variety of needs. Key features include:
17-4PH alloy features excellent corrosion resistance, superior to any other hardenable stainless steel. In most cases, it has as good corrosion resistance as type 304. Despite this, stress corrosion can happen under a high-strength state; if there is a risk of stress corrosion cracking, it will be necessary to adjust the stabilization temperature. The alloy 17-4PH is susceptible to corrosion or crack corrosion in static seawater. However, in the petrochemical, food processing and paper industries, its corrosion resistance matches grade 304L
17-4PH embodies the advantages of austenitic steel after solution treatment and is easy to work with. It can obtain high strength through intermediate pressure treatment and aging treatment, so it is widely used in pressure vessels, aircraft and steam turbine blades. It is mainly used for these parts because they are either in contact with the medium or highly stressed. For example, if the impeller is in direct contact with the medium, it poses high requirements on the corrosion resistance of the material used. Since the shaft must drive the rotor components such as the impeller to rotate together, it is subject to large force, requiring very good strength and toughness to operate. The mechanical properties required for its materials, hence, must be very good. That’s how 17-4PH comes into play as its corrosion resistance and mechanical properties meet these two requirements.
The density of 17-4 stainless steel is 0.280 lb/in3 (7.8 g/cm3), which makes it an ideal material for many applications that require high strength and corrosion resistance.
One of the most important properties of 17-4 PH is that it offers superior hardness when heat treated, making it an ideal choice for applications that require high strength and wear resistance.
17-4 stainless steel is highly versatile due to its machinability. The metal alloy can be used for a wide variety of purposes and applications across industries.
Also called precipitation hardening, age hardening uses existing particles or solid impurities to increase the strength of an alloy. 17-4 stainless steel is well-suited for this process.
To age harden 17-4 stainless steel PH, you would first use a solution treatment, then quenching and aging. The treatment needs to be performed at 1050 °C for 30 minutes. To complete precipitation hardening, the temperature ranges from 480 °C to 760 °C and usually takes two to four hours.
Achieve superior hardness from welding after heat treatment. Machining conditions differ with the firmness of the element.
Different levels of strength and hardness can be achieved depending on the temperature it is heat treated at. The ASTM designation is A564 and common conditions are H900, H1025, H1075, H1150, and H1150D.
17-4 stainless steel is renowned for its exceptional strength, corrosion resistance and durability. Due to these characteristics, 17-4 PH stainless steel is frequently utilised in the aerospace, medical, and food processing industries, as well as in construction, oil and gas, and transportation. Furthermore, the alloy is commonly employed in the manufacture of gears, valves, pumps, and fasteners, as well as in the production of moulds and dies.
The alloy's high strength and corrosion resistance properties make it an optimal material for use in harsh and demanding environments.
17-4PH finds use in various industries. Typical parts include mechanical seals, oil patch, and pump shafts.
Furthermore, the alloy also finds use in the aerospace industry, petroleum industry, and chemical industry, food processing equipment, paper and pulp industry, nuclear waste processing and storage, and general metalworking.
Sunny Steel offers Stainless Steel 17-4PH in two sub-type specifications and multiple shapes/forms:
17-4 stainless steel is an excellent choice for the oil and gas industry due to its ability to withstand harsh conditions and corrosive environments. The alloy is highly resistant to corrosion caused by saltwater and chemicals, making it ideal for use in offshore and coastal environments.
Furthermore, 17-4 stainless steel has a high strength-to-weight ratio, which makes it an optimal choice for use in the oil and gas industry where weight and size are often critical factors.
The inclusion of molybdenum in 316 stainless steel enhances its corrosion resistance and improves its mechanical properties. 316 steel is suitable for marine or coastal environments and resists chloride ion corrosion or saltwater corrosion.
410 stainless steel is a cost-effective alternative to 316 that provides good overall performance and is suited for valves, dies, screws, and fasteners.
While 420 steel offers enhanced durability and strength compared to 410 stainless steel, the latter is more suitable for applications that require precision machining due to its ductility.
In the food processing industry, corrosion-resistant 17-4 stainless steel is frequently employed in the manufacture of food processing equipment, including storage tanks, conveyors, and processing machinery. The alloy exhibits magnetic properties, making it an optimal choice for use in food environments where magnets are utilised to facilitate the removal of contaminants.
Furthermore, the high strength and durability of 17-4 stainless steel make it an excellent option for applications that require frequent sanitation and cleaning processes.
In the paper and pulp industry, 17-4 stainless steel is used when creating equipment that processes pulp such as tanks, pumps, valves, and heat exchangers. Because the parts may be exposed to high temperatures, it’s important to use a resilient alloy like 17-4.

This stainless steel alloy is suitable for incorporation into parts requiring hardness and corrosion resistance at temperatures below 600°F (316°C), regardless of the industry in question. Potential applications include:
17-4 stainless steel may not be the optimal choice for the task at hand. At Premium Alloys, we offer a range of suitable materials for your project. However, how does stainless steel compare to the alternatives?
17-4 stainless steel and 15-5 stainless steel are both precipitation-hardened alloys that are known for their high strength, corrosion resistance, and toughness. 17-4 stainless steel contains 17% chromium and 4% nickel, while 15-5 stainless steel is composed of 15% chromium and 5% nickel.
Stainless steels in the 300 series have 18 to 30% chromium and 6 to 20% nickel. While the metal is also resilient and versatile, it can’t be heat treated to as high of a temperature as PH 17-4 can.
17-4 stainless steel is significantly stronger than 416. In fact, it has more than 4 times the resistance of 416 steel.
17-4 alloy steel has many benefits in a number of industries, including manufacturing and chemical processing. Compared to some other types of stainless steel, 17-4 has superior strength, toughness, wear resistance, and fatigue strength.
17-4 stainless steel is highly customizable, making it an ideal choice for a variety of applications from aerospace to food processing. Stainless steel 17 4 PH properties allow the alloy to be tailored to suit the specific requirements of any given task.
17-4 steel is extremely strong, offering a very high yield strength of up to 1100-1300 MPa (160-190 ksi).
The metal also offers good weldability when welded with processes like shielded fusion and resistance welding.
Stainless steel alloy 17-4 PH is excellent at withstanding corrosive attacks, and it performs better than other standard hardenable stainless steels. Because of this, it is widely used in applications like food preparation equipment, aerospace components, oil and gas, and chemical processing.
17-4 PH stainless steel is known for providing superior toughness, and strength over a range of temperatures. With a low thermal expansion rate, 17-4 steel can develop a high magnetic permeability, with applications requiring higher levels including cores, efficient motor laminations, and more.
This material provides excellent protection in extreme environments, making it the perfect choice for applications that require high levels of durability.
Since the metal is highly resistant to corrosion, it can be used for radioactive storage. With its unique strength and resistance properties, 17-4 stainless steel PH is an ideal material for buildings that store hazardous materials.
The discovery of metals has resulted in the production of many products that are part and parcel of our daily lives. Metals are used in manufacturing items such as an ordinary saucepan to space-going vessels. Individual metals tend to have certain characteristics and properties. Certain components need elements with particular properties. When a metal is unable to be suited to a particular application, it is combined with one or more elements resulting in an alloy.
Stainless steel is an example of a common alloy used in the fabrication of many products. To further strengthen the stainless steel, they are subjected to heat treatments which result in the precipitation hardening stainless steel material. One of the most used types of PH stainless steel is 17-4 PH stainless steel.
There are many things that you probably did not know about the alloy? Take heart, though. You will be amazed by how much you did not know about the most commonly used types of stainless steel. The following are seven things that you probably did not know about type 17-4 PH stainless steel:
PH stainless steels are a group of alloys that are resistant to the effects of corrosion. To increase their yield strength, these alloys are subjected to heat treatment during precipitation hardening (PH) or age hardening.
You must be wondering what all these terminologies mean. Usually, PH alloys are kept at elevated temperatures for an extended time frame. This allows precipitation to take place.
Hopefully, you remember your elementary science classes at this point. This aging or time-delayed technique tends to significantly increase the alloys yield strength.
During PH-treating, certain “impure” particles are added to the stainless steel. Such particles include elements such as molybdenum, copper, titanium or aluminum, either in combination or singly.
There are three main types of PH stainless steel, namely:
Type 17-4 PH stainless steel is the most common type of martensitic PH stainless steel. At low temperatures of 250 degrees Centigrade, the martensitic alloy transforms to martensite. Martensite is basically a steel crystalline structure that is hard.
The stainless steel alloy can harden further by aging at temperatures ranging between 480-620 degrees Centigrade. The combination of the alloy’s superior properties allows it to increase product reliability while making fabrication simple and cost effective. Type 17-4 PH stainless steel has applications in industries like paper, petrochemical, aerospace and food processing. It is widely used in various general metalwork applications.
The alloy has superior resistance to corrosion and has high mechanical strength. This enables it to be used in marine applications. The fact that it is resistant to corrosion enables it to survive exposure to salty sea water.
You should know that one of the elements that confer the alloy with high resistance is chromium. Type 17-4 PH stainless steel contains between 15-17.5% of chromium in its composition. In this regard, a seagoing vessel’s pump and valve parts are made of type 17-4 PH stainless steel.
Most of the parts of that ship that you went on that annual cruise are made from type 17-4 PH stainless steel. Most of the process piping, seawater piping, and heat exchangers are made of the alloy.
Did you know that the alloy has been used in the nuclear power generation industry? Well, what usually happens during nuclear power generation is there is the use of fuel during the process. The used fuel should be given some time to cool and be stored. Used or spent fuel from nuclear power generation is stored in a dry cask.
The dry cask is usually fabricated using type 17-4 PH stainless steel. The spent fuel in the cask has an inert gas surrounding layer. The steel cylinder cask is usually butted or welded closed. The great welding characteristics of the alloy allow this to be possible.
This design of the dry cask using type 17-4 PH stainless steel ensures that the radioactive spent fuel is in a safe storage design that is 100% leak proof. To ensure that there is adequate radiation shielding for you, in case you work in such a plant, reinforcement is achieved using extra steel, concrete or other material.
To increase its strength during PH treatment, some elements are added to the stainless steel. The composition of type 17-4 PH stainless steel is as follows:
As a result of its composition and depending on the temperature, the alloys are able to develop various properties.The versatility of the alloy makes it quite popular in industries like the pulp and paper. In the past, you may have noticed that paper mills were made of materials such as carbon steel, bronze, and granite. Well, not anymore.
In the manufacture of paper, batch digesters are important pieces of equipment. What batch digesters do is they manufacture solid pulp products. The paper that you use every day to write on is then made from these pulp products. In the past, bulk digesters in the pulp and paper industry required plants to shut down at least every 18 months for routine maintenance. Currently, such bulk digesters are made of stainless steel.
You will find that stainless steel bulk digesters are much thinner than their carbon steel counterparts. This is because type 17-4 PH stainless steel has a higher yield pressure than carbon steel.
Corrosion of carbon steel digesters has been a perennial design problem. The use of type 17-4 PH stainless steel, which has a high resistance to corrosion, has been of great significant value in the paper industry. As you can see, this also reduces costs because the equipment will not succumb to the effects of corrosion and breakdown.
The next time you see a gas or windmill turbine at work, try and remember that it works because of the use of type 17-4 PH stainless steel in its construction.
In case you are familiar with the design of a turbine, then you are familiar with a combustor. If not, a combustor produces gas at a high pressure and temperature. It is the turbine blades that extract the energy that you need from these gasses.
As you can see, the turbine blade material should be able to withstand the harsh conditions of high heat and pressure. In the past, one of the common causes of failure in turbine blades was a stress material failure and fatigue.
Current turbine blade design makes use of super-alloys like type 17-4 PH stainless steel. The fact that the alloy has a high resistance and is able to keep its strength under adverse conditions like high temperatures makes it an ideal choice in turbine blade design.
Most plane engine manufacturers like Pratt and Whitney or Rolls Royce make use of the alloy when designing the turbine blades for their massive engine.
In case you work in the food and beverage industry, then you should know that most of the equipment that you use is made from stainless steel. The type 17-4 PH stainless steel is used in equipment for the processing and manufacture of foods and beverages.
The fact that the alloy has a good surface condition and great finish makes it an ideal choice. The alloy’s smooth surface and high chromium content make it less prone to corrosion and makes it easy to clean as hygiene is an integral element of food and beverage manufacture.
Did you know that the alloy is a significant part of the oil and gas industry? There are two main reasons why the alloy is used:
First, Oil is usually obtained at great depths, below sea level. Such depths are associated with high pressure. The high strength of type 17-4 PH stainless steel makes it a great construction material for piping at such depths.
Second, Type 17-4 PH alloy is resistant to corrosion both on and offshore. Its resistance to corrosive media like hydrogen sulfide gas, carbon dioxide and low pH levels in oil prospecting conditions makes it the material of choice for oil rigs and pipes.
It is quite evident that type 17-4 PH stainless steel is the most used type of PH stainless steel. It has an ideal combination of corrosion resistance, good mechanical properties at high temperatures and high yield strength. This combination makes it a suitable alloy for many applications. Its superior properties and cost effectiveness makes it the best, most used type of stainless steel.
Annealed hot treatment : 17-4PH Bright Bar with hardness HRC 30-34 , waiting for your inquiries.









17-4 PH® is a martensitic precipitation hardening stainless steel offering high strength and hardness along with moderate corrosion resistance up to 600˚F. It has good fabrication characteristics and can be age hardened using a single heat treatment in the 900-1150˚F temperature range. This grade has been used for a variety of oil field and chemical process equipment, as well as fittings and fasteners.
Our 17-4 stainless steel round bar supply ranges from 1/8” to 24” in diameter. As an industry leader in long-length stainless steel bar, we provide the perfect stock for your needs.
Our 17-4 PH square bar stock is comprehensive and comes in a number of square bar grades, like 300 Series and 400 Series.
As a leading stainless steel bar distributor to the pump manufacturing industry, Best Stainless provides high-quality, 17-4 pump shaft bar in several common grades and sizes.
From Precipitation Hardening grades to Duplex Stainless Steel grades, our stainless steel flat bars are high-quality and can be used for a variety of applications.
Our 17-4 ph stainless steel hexagon bar comes in several grades and can be cut to your specific needed size for any project or application.
Best Stainless supplies a variety of boat shaft stainless steel bars in long lengths and oversized to finish.

When you partner with Sunny Steel, you can stop worrying about meeting deadlines thanks to our responsive and timely service. You'll also say goodbye to unnecessary shopping around. Instead, you'll get white glove service from an expert who understands your needs and can get you the materials you need quickly.
