Nipo Flange
Nipoflange is a connection that has a flange on one side and a Nipolet on the other side.
Carbon steel flanges are made from carbon steel, which is an alloy composed primarily of iron and carbon.
Carbon steel flanges are essential components in various industrial applications due to their strength, durability, and versatility. These flanges are used to connect pipes, valves, pumps, and other equipment, forming a secure and reliable piping system. The material used in these flanges, carbon steel, is valued for its high strength-to-weight ratio and ability to withstand high pressures and temperatures.
Common standards include ASTM A694, ASTM A105N (SA105N), MSS SP-44, DIN 2533. Accompanying pressure ratings are from class 150 to 2500.
Carbon steel is a steel with carbon content up to 2.1% by weight. Where in AISI defines:
As carbon element content increases, the steel will become harder and stronger after heat treatment. On the contrary, it become less ductile. Where if without heat treatment, higher carbon will reduce weldability.
Carbon steel may include alloy steels in case it is not used as stainless steel.
Carbon steel flanges are a type of piping component used to connect pipes or other equipment in various industries. They are made from carbon steel, which is an alloy composed primarily of iron and carbon. Carbon steel flanges are known for their strength, durability, and affordability.
Carbon steel flanges are commonly used in industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and water treatment, where strength and toughness are important considerations. The choice of carbon steel grade depends on several factors, including the application, the environment, and the required performance characteristics.
Overall, carbon steel flanges are an essential component of industrial piping systems, providing a means to connect pipes and other equipment components in a secure and leak-proof manner.
Carbon steel pipe flanges usually adopt mild steel or low carbon steel, as it includes small percentage of carbon, strong and tough but not readily tempered. Which with lower cost and material could be used for many applications.
Carbon steel flanges are widely used across various industries due to their adaptability and reliability. Common applications include:
Carbon steel flanges also ranged with slip on flange, weld neck flange, blind flange, socket weld flange and threaded pipe flange.
ASTM A105 steel grade is a typical common material (mild carbon steel) for forged carbon steel flange, it used in a lot of places for ambient and higher-temperature service in pressure systems. This material is durable, cost lower, and difficult to break. In case used in a stainless steel piping system it shall be adapted with a lap joint end ring.
Designed specifically for low-temperature usage, this carbon steel grade shares close similarities with ASTM A105N (SA105N) grade. This grade requires notch durability testing, and applicable for many industries.
This carbon steel grade also applied to low temperature carbon steel fittings.
The standards set for ASTM A694 is more rigorous than the two above. Its requirements for high-pressure fluid transmission of oil and gas piping is stringent. Because of the stringent conditions with the steel grade, manufacturers have to develop an even stronger steel for both low temperatures and high temperatures. There is a minimum yield strength that comes with all grade of A694.
Carbon Steel Flanges are manufactured either by forging or by casting.
There are several types of coatings to protect carbon steel flange from rusting or corrosion:
Forgings made from A-105 grades are the first and most common materials used to manufacture pipe flanges. For applications requiring lower temperatures, the A-350 LF2 grades are used, while the A-694 grades, F42-F70, are designed for high yields. Due to the increased strength of carbon steel flanges, high yield material is widely used in pipeline applications.
In addition to containing more chromium and molybdenum than carbon steel flanges, alloy steel flanges are designed to withstand high temperature and high pressure environments. Because of the increased chromium content, they have stronger corrosion protection than conventional carbon steel flanges.
Stainless steel containing nickel, chromium and molybdenum is the second most commonly used forging material in flange manufacturing. The most common ASTM A182-F304 / F304L and A182-F316 / F316L forgings are found in the A182-F300/F400 series. Trace elements can be added during the melting process to meet the service requirements of these forging classes. In addition, the 300 series is non-magnetic while the 400 series has magnetic properties and is less corrosion resistant.
Pipe Flange Standards mainly include three systems in the world, ANSI/ASME flange system(American), DIN flange system(European system), JIS flange system, other system made according to this three systems, like GB flange standard, which mainly made according to ANSI/ASME and DIN flange standard, Duwa Piping supplies those flanges with top quality and soonest delivery time.
The most frequently asked questions regarding flanges and flange fittings have to do with how flanges fit on specific steel tube and steel pipe ends.

Flanges have flat or flush surfaces that are vertical to the pipe to which they are attached. The attachment process involves mechanically joining two or more faces using bolts, adhesives, collars, or welds. Due to the attachment requirements, a flange must fit the equipment or pipe that it’s designed. That’s why it’s necessary to check all the possible specifications and dimensions to ascertain that it’s of the right size, type, and material.
Pipe flanges, gaskets, and bolts are the three parts that comprise a flanged connection. Gaskets and bolts are typically made of the same flange materials or a material approved for the pipe components. Each component comes in various materials that suit specific applications and must be matched correctly for proper functioning. The gaskets come in two conventional types: full-face gaskets and ring gaskets. Full-face gaskets have the bolt holes visible and pair up with raised-face gaskets. Ring gaskets tend to be smaller rings minus the bolt holes and pair up with flat-faced flanges. Securing the flange components requires matching the surfaces evenly and plumb, adjusting as needed for a uniform fit. Once all surfaces match, bring the flanges together and secure at least two of the bolts. Refine the alignment, so the remaining bolt holes match and their corresponding bolts are tightly secured.
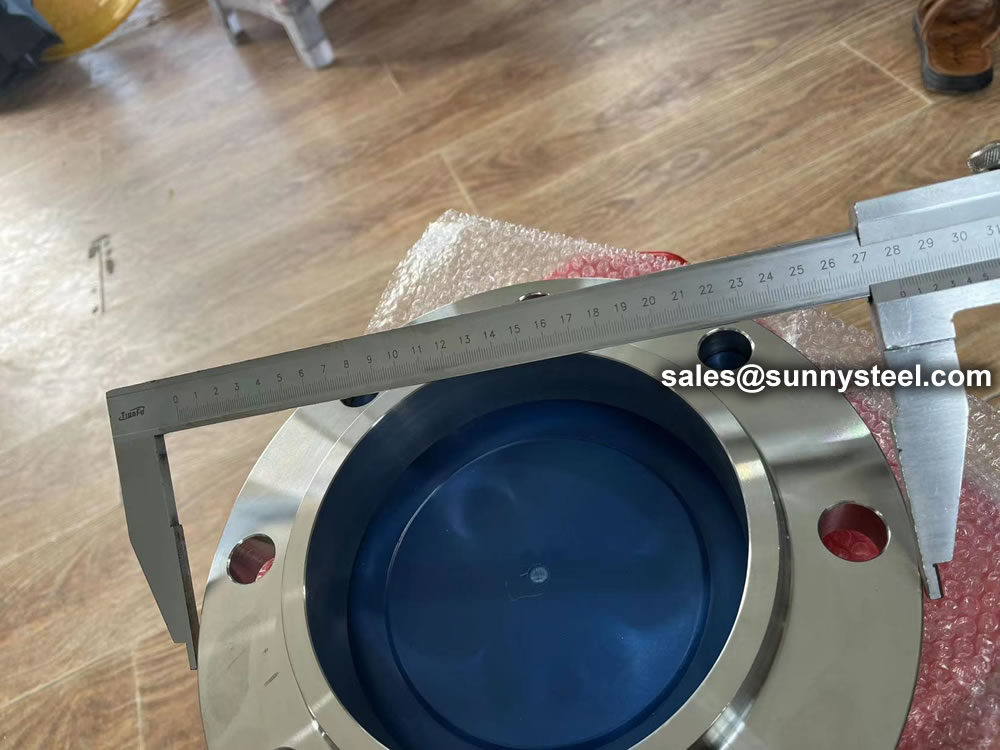
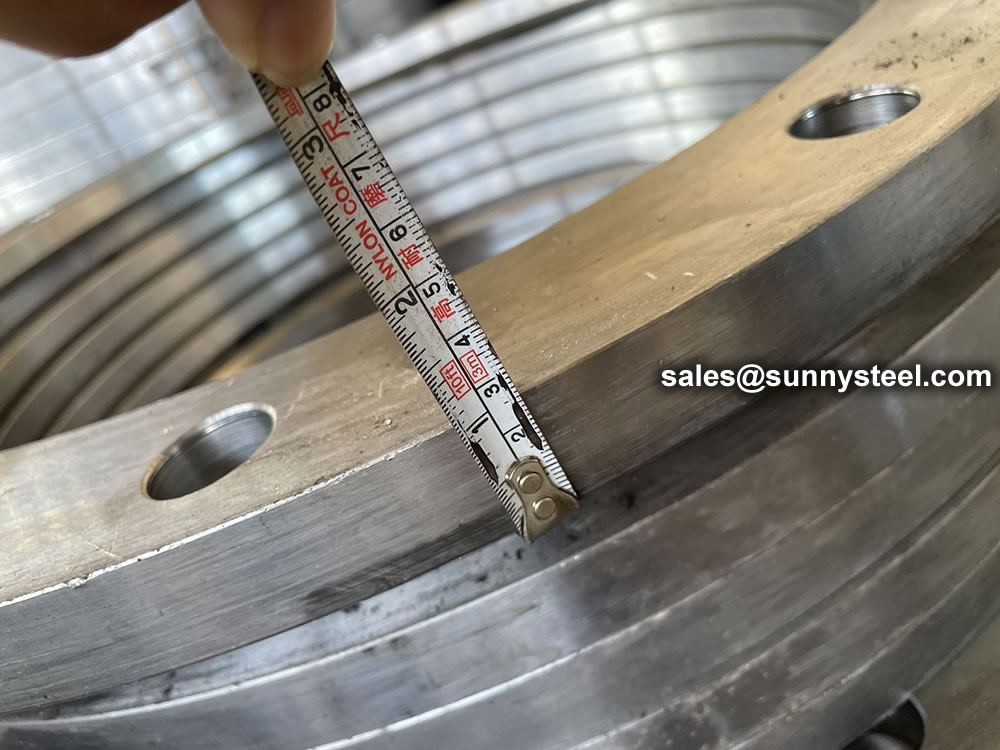
Properly sizing a flange for pipe use depends not only on the type of flange but its compatible piping. The pipe must slip into the flange’s inside diameter easily and securely, and the outside diameter should cover wall holes. Once you determine the specific flange type and material you need for the job, you’ll need to take several measurements. The four measurements you’ll need are the inside diameter, outside diameter, bolt hole count, and bolt hole center. You’ll need to align each of these measurements from opposing bolt holes to get the most accurate readings. Take all measurements from edge to edge and try to get as precise as possible to match the correct product. Round up bolt diameter to the next half or whole step since bolts measure half or whole inches. Once you have all four measurements, check them against the manufacturer’s table to find the correct flange. Most manufacturers list these specifications on their websites for easy reference.
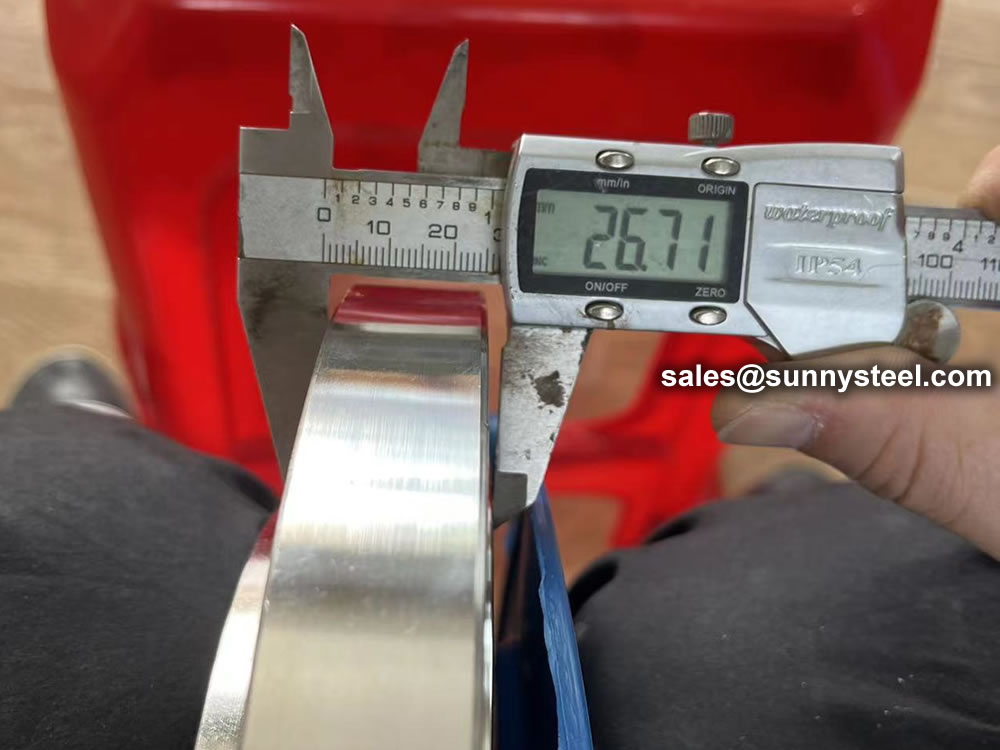
Before dispatching from manufacture each flange is inspected to ensure quality. During an inspection you have to check the following;
ASME B16.5 and B16.47 standards cover permissible tolerances for inspection.
Flanges are used to connect pipes or other equipment components in various industries, and they come in a variety of materials and sizes. Flange material standards are developed by standard-setting organizations and describe the properties and characteristics of different materials that can be used to make flanges. Some examples of commonly used flange material standards include:
The choice of flange material standard will depend on various factors such as the application, the environment, the fluid being transported, and the required performance characteristics. For example, high-pressure applications may require flanges made from materials with high strength and durability, while corrosive environments may require flanges made from materials with good resistance to corrosion.

There are many ways to connect flanges, including threading, welding or bolting. The threaded flange is best for low pressure or smaller pipelines because it can maintain its seal. When your pipeline is larger or high pressure, then the welded flange is preferable. A boiler room is one place where welded blind flanges might be used, due to the high pressure involved.
Flanged joints: flanges, bolts and nuts and gaskets
A flange is a external rib at the end of pipes, valves and other flow devices to assemble them.
Dimensions of the flanges are up to specific Standards : DIN, ANSI, AS, BS, JIS
A flanged connection requires two flanges (the “main” and the “companion”), a set of bolts and nuts (whose number depends on the flange diameter and class) and two sealing gaskets. Flanged connections have to be executed and supervised by trained personnel, as the quality of the joint has a critical impact on the performance of the piping system / pipeline (the standard TSE – TS EN 1591 Part 1-4, “Flanges and their joints”, defines a number of requirements for the execution of proper flanged connections). Whereas all elements of the joint are critical, experience shows most leaks are originated by the improper installation of the sealing elements, i.e. the gaskets.
The typical pipe to flange connections are welded or threaded. Welded flanges are used for pipelines and piping systems with high pressures and temperatures, and with diameters above 2 inches.
Threaded connections are instead used for installations of smaller diameter and not subject to severe mechanical forces such as expansion, vibration, contraction, oscillation (forces that would crack the threaded joint). In all these critical cases, butt weld connections are recommended.
Steel flanges must be packed with seaworthy packing method then delivery to customers, usually the packing way include wooden box, wooden pallet, iron & steel cage, iron & steel pallet etc.

Flange markings are governed by ANSI ASME codes. Flange marking includes;
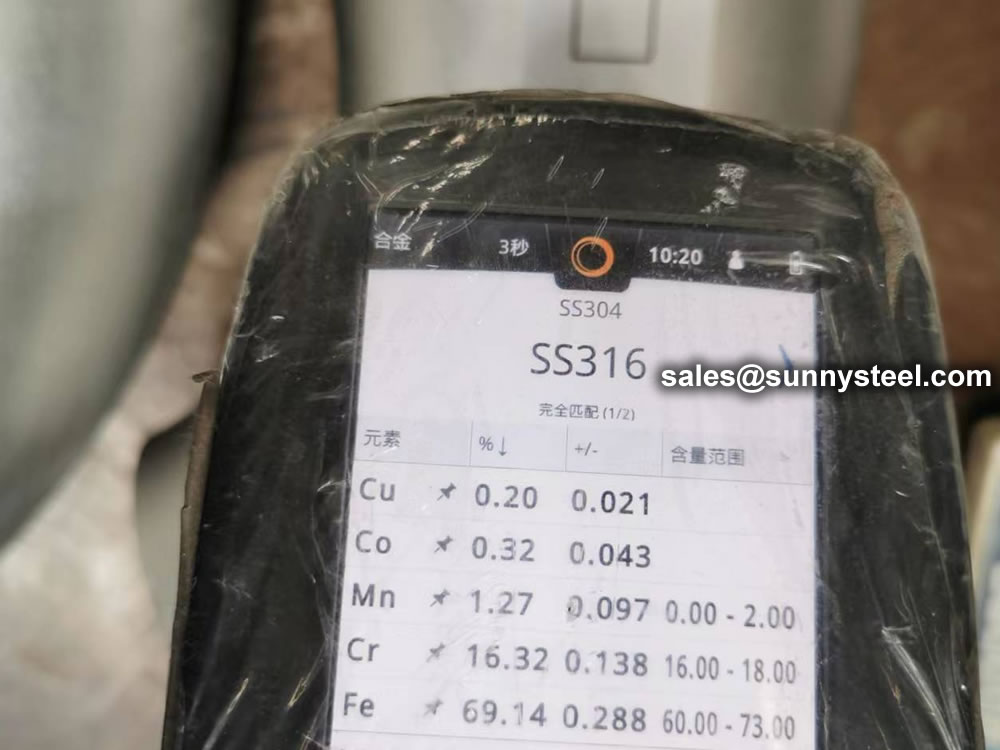

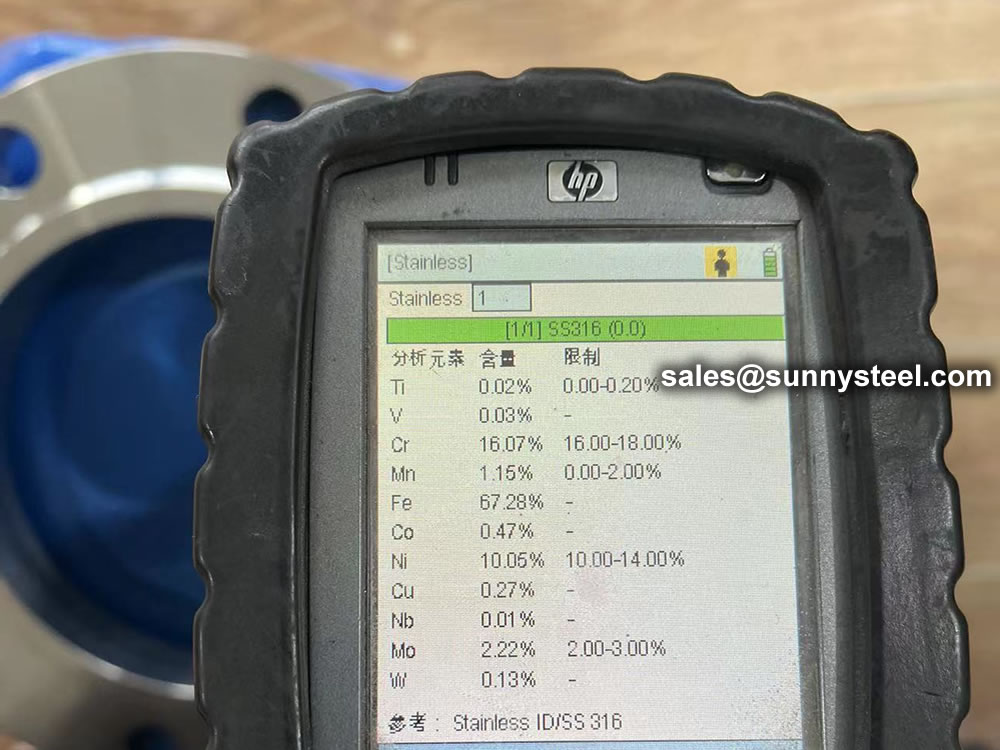
ASME B16.5 and B16.47 standards cover permissible tolerances for inspection.






Because of the normal wooden boxes or wooden pallets have to do fumigation treatment, we usually use plywood pallet or plywood case or box to pack steel flanges without fumigation treatment.







When you partner with Sunny Steel, you can stop worrying about meeting deadlines thanks to our responsive and timely service. You'll also say goodbye to unnecessary shopping around. Instead, you'll get white glove service from an expert who understands your needs and can get you the materials you need quickly.
